Building an incentive package

Incentives for Ecosystem Services (IES) exist in different forms and from different stakeholders, but work together as a complete package. Each stakeholder invests in the scheme for its own purpose, but towards a common goal. To ensure sustainability, it is best to diversify the ways to provide incentives and the incentive mechanisms. IES can enable the public, private and civil society sectors reach mutually beneficial environmental and rural development targets. Together, they can finance and support an integrated package of short and long term incentives that effectively protects ecosystem services and assists in the long-term transition to sustainable agriculture.
IES links stewards of ecosystem services, such as farmers, with their beneficiaries, such as communities, private businesses, NGOs and governments. IES can support landowners to protect the environment and maintain their livelihoods through sustainable agricultural practices. For example, with: Short-term incentives such as improved seeds, organic fertilizer, and irrigation so that farmers improve productivity and require less land for cultivation and can implement conservation practices; and, Long-term incentives, such as improved storage and processing, combined with improved access to markets, to render the sustainable practices worth it in the long-run.
The following stakeholders can combine their efforts to offer these incentives:
- Public programmes investing in improved seeds and breeds, as well as access to marketing and rural credit, to conserve public goods.
- Private companies contributing to rural enterprises for their corporate social responsibility and to offset negative environmental impacts.
- Civil society initiatives supporting producer cooperatives, development of alternative livelihoods and investment in social protection.
- Water-user fees used for riparian vegetation regeneration
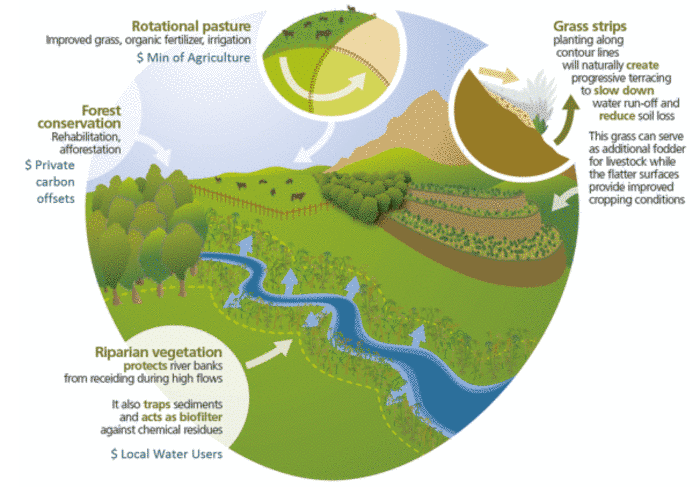
- Map highlighting sources of possible co-financing from different users of ecosystem services provided by agriculture and where they could be implemented.
