When the cocoa trees have been planted, the work is not finished.
The grower still has a lot of work to do to look after his cocoa trees.
A grower who does not look after his plantation properly cannot harvest big pods and will not earn much money.
To look after your plantation properly you must:
Replace seedlings that have not grown
Remove weeds and keep the soil covered
Prune the cocoa trees
Apply fertilizer
Protect the cocoa trees from insects and diseases.
Sometimes certain cocoa seedlings do not grow well. They remain small or die.
During the months following the day when you planted
your seedlings, you must always look to see
whether the cocoa trees are growing well.
If you see diseased or dead cocoa trees, pull them
out and burn them, and also those encircling them
in case of swollen shoot disease (see paragraph 42).
In their place, plant other young cocoa seedlings,
from among those that you have kept in the nursery
bed or in baskets.
Many weeds grow among the cocoa tree rows.
You must not let weeds take nourishment away from
the cocoa trees.
When the cocoa trees are young, you should weed
4 or 5 times every year.
When the cocoa trees are bigger, they cast a lot
of shade and so few weeds will grow.
It will be enough to weed once a year.
When you are cultivating be very careful not to
damage the trunk and roots of the cocoa trees.
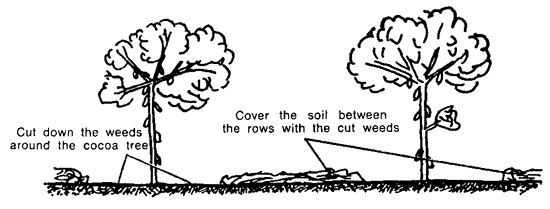
Between the rows of cocoa trees, you should not leave the soil bare.
You should cover the soil either with cut weeds or
with palm fronds, if available.
In this way the soil is protected against sun and erosion;
it stays moist and cool.
When the weeds rot, they give the soil organic matter.
You can also sow a cover crop, for Instance legumes.
This will give the soil good protection against sun and
erosion.
The cocoa tree is a tree that develops well.
It has a single, straight trunk.
A crown of 3 to 5 main branches forms about 1.5
metres above ground level.
Sometimes, during the first year, several shoots form
on the trunk.
Cut off these shoots and leave only the strongest.
Sometimes the crown forms too low down, at less
than 1 metre above ground level.
Choose a shoot which grows straight up and let it
develop.
A new crown will then form at a good height, and
the first crown will stop growing.
| Young well-grown cocoa tree |  |
 |  |
| Young cocoa tree with two shoots | Cocoa tree which forms its crown too low down |
Always cut out all dead branches, dry twigs and suckers.
A sucker is a twig that grows upward out of the trunk.
Cut off the suckers very close to the trunk.

When a cocoa tree gets old, it no longer yields many pods.
But you can make cocoa trees young again by letting
one or two suckers grow low down on the trunk
where they can develop their own roots.
Then cut down the old trunk, and you will again have
a cocoa tree that yields many pods.

Fertilizers cost a lot of money.
So the grower should use fertilizers only when this will
make him earn more money.
When you have tended your cocoa trees, when you have hoed the weeds, then you should apply fertilizer.
Spread fertilizer around each cocoa tree, but be careful not to put any on the trunk, the branches or the leaves of the cocoa tree: otherwise the fertilizer will burn the tree.
Spread the fertilizer in a ring around the trunk at a
distance of about 1 metre from it, where most of its
small roots are.
Apply fertilizer twice a year: in April and September.

It Is useless to apply fertilizers in a plantation that is not well cared for.
A grower who does not prune his cocoa trees and
who does not hoe the weeds should not apply any
fertilizer.
If the plantation is not cared for properly, fertilizers
do nothing except feed the trunks of the cocoa trees,
the suckers and the weeds.
The grower loses his money.
Different soils have different fertilizer needs.
Ask the extension service how much fertilizer to use.
For example, in Ivory Coast:
on the more sandy soils, along the coast, use compound fertilizer, which contains nitrogen, phosphoric acid and potash: fertilizer formula 13-10-15;
on the more granitic soils of the interior, use another compound fertilizer: formula 12-15-18.
The quantities for each tree are as follows:
during the first two years:
in April: 125 grammes;
in September: 125 grammes.
during the third year and from then on:
in April: 250 grammes;
in September: 250 grammes.
The most dangerous insects are the following:
Capsids
These insects prick the twigs and pods.
At the place where they make a hole, the tree dries
out and the sap no longer circulates.
Young trees attacked by capsids often die.
To control capsids, use Lindane or Aldrin.
Borers
The larvae of these insects bore holes in the trunk
or branches.
You can control borers with DDT or Dieldrin.
 |  |
| Capsid | Borer |
The most dangerous diseases that attack cocoa trees are the following:
Black pod disease
This is caused by a fungus which chiefly attacks the
pods.
If attacked, the pods rot and die.
Control this disease by picking off diseased pods and
burning them.
You can prevent the disease from spreading by
spraying the sound pods with copper preparations.
Swollen shoot disease
This is a very serious disease, which has caused much
damage in Ghana.
You will see that the leaves are mottled. Sometimes
some twigs become very thick and the tree soon dies.
Mealy bugs carried about by ants can transmit the
disease from one tree to another.
Control this disease by cutting down diseased trees
and leaving them to wither.
Remember that, when a diseased tree has been discovered
and cut down, all the trees circling it must
be cut down also to avoid the spread of infection.