Big refrigerator +4°C;
Deep freezer -27°C;
Cold room;
100 g balance (Mettler);
Electrophoretic instrument for immune-electrophoresis;
High-speed centrifuge;
Micropipettes (5-10-25-50-100 μ1);
Sonicator;
Cages for rabbits and room with water and heating;
pH meter with drop-electrodes, combined electrode;
Stabilized power supply, with 500–1 000 volts;
Shaker for producing large amount of bacteria;
Chemicals.
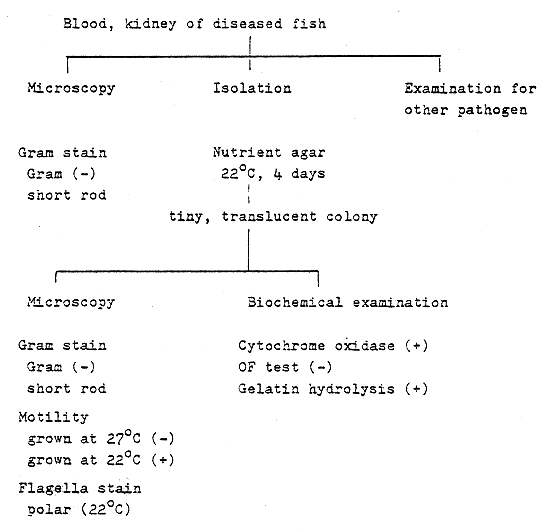
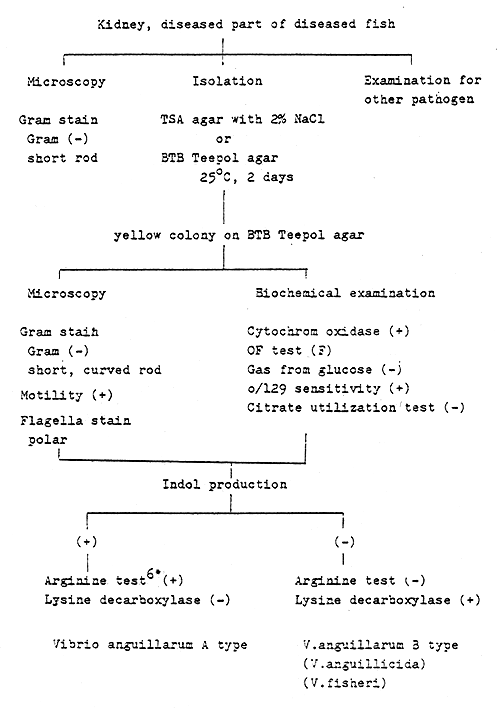
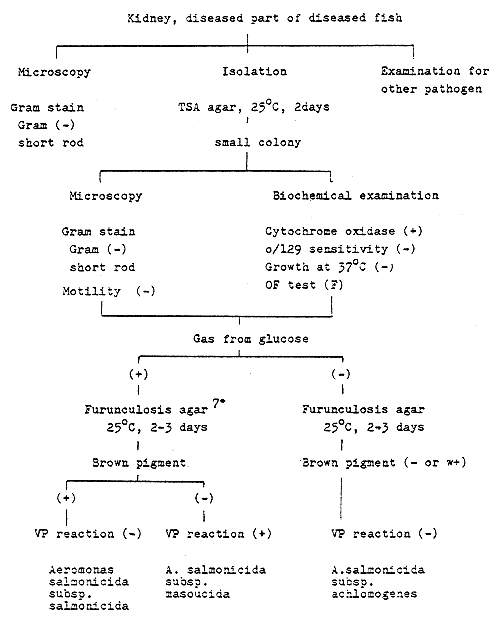
Fig. 1 - The rapid identification procedure for Aeromonas spp.
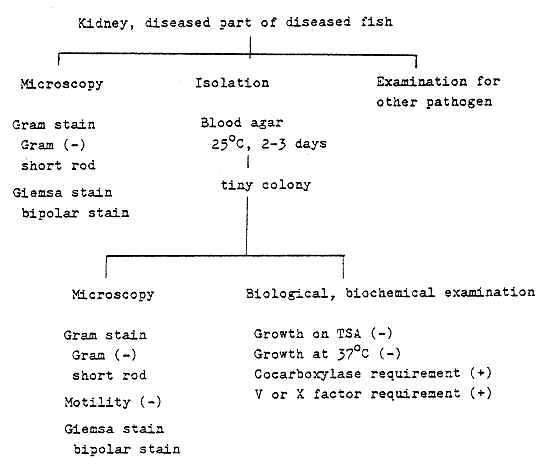
Aeromonas spp. (Carp - red spot disease, Eel - red fin disease)
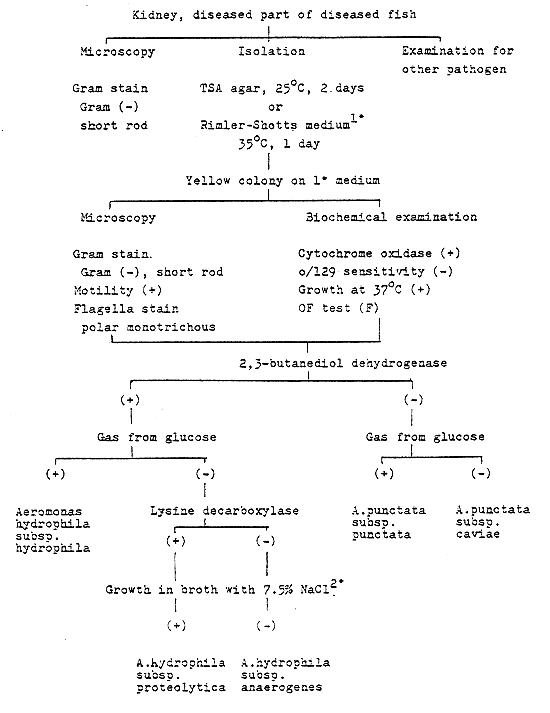
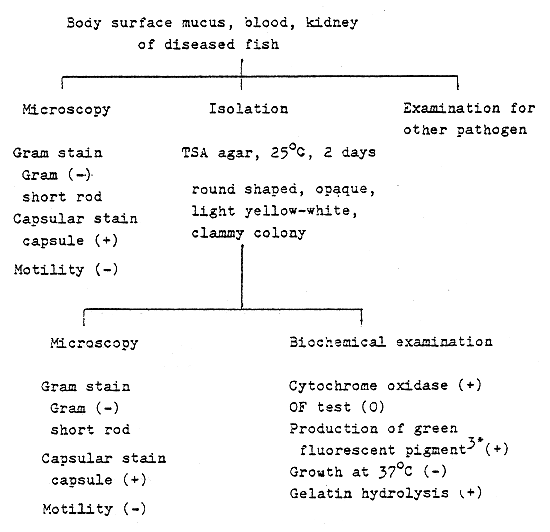
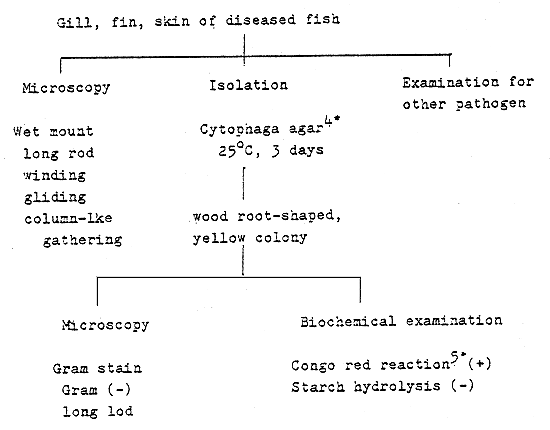
Fig. 2 - The rapid identification for Pseudomonas sp.
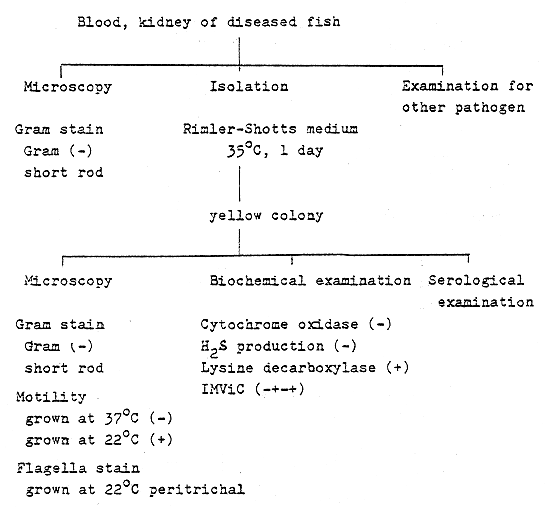
Pseudomonas sp. (Carp - pseudomonas infection)

| 1*. Rimler-Shotts medium | |||
| L-lysine hydrochloride | 5.0g | ||
| L-ornithine hydrochloride | 6.5g | ||
| Maltose | 3.5g | ||
| Sodium thiosulfate | 0.3g | ||
| Bromthymol blue | 0.03g | ||
| Iron ammonium sulfate | 0.8g | ||
| Sodium deoxycholate | 1.0g | ||
| Novobiocine | 0.05g | ||
| Yeast extract | 3.0g | ||
| Sodium chloride | 5.0g | ||
| Agar | 13.5g | ||
| Distilled water | 1000 ml | ||
| pH | 7.0 | ||
| 2*. Broth with 7.5% NaCl | |||
| Peptone | 10.0g | ||
| Sodium chloride | 75.0g | ||
| Distilled water | 1000 ml | ||
| 3*. Production of green fluorescent pigment | |||
| Cultivation on King's medium* | |||
| 25°C, 1 week | |||
| ↓ | |||
| Production of yellow-green fluorescence | |||
* King's medium | |||
Peptone | 20.0g | ||
Potassium phosphate monobasic | 1.5g | ||
Magnesium sulfate | 1.5g | ||
Glycerin | 10.0g | ||
Agar | 15.0g | ||
Distilled water | 1000 ml | ||
pH | 7.2 | ||
| 4*. Cytophaga agar | |||
| Tryptone | 0.5g | ||
| Yeast extract | 0.5g | ||
| Beef extract | 0.2g | ||
| Sodium acetate | 0.2g | ||
| Agar | 9.0g | ||
| Distilled water | 1000 ml | ||
| pH | 7.2–7.4 | ||
| 5*. Congo red reaction | |||
| Colony on cytophaga agar | |||
| ↓← 0.01% Congo red solusion | |||
| Edge of the colony | |||
| ↓ | |||
| Turning red (+) | |||
| 6*. Arginine test | |||
 | |||
| 25°C, 3–7 days | * Arginine agar | ||
| ↓ | |||
| Turning red (+) | Peptone | 1.0g | |
Sodium chloride | 5.0g | ||
Potassium phosphate dibasic | 0.3g | ||
Phenol red | 0.01g | ||
L-arginine hydrochloride | 10.0g | ||
Agar | 3.0g | ||
Distilled water | 1000 ml | ||
pH | 7.4 | ||
| 7*. Furunculosis agar | |||||
| Tryptone | 10.0g | ||||
| Yeast extract | 5.0g | ||||
| L-tyrosine | 1.0g | ||||
| Sodium chloride | 2.5g | ||||
| Agar | 15.0g | ||||
| Distilled water | 1000 ml | ||||
| pH | 7.5 | ||||
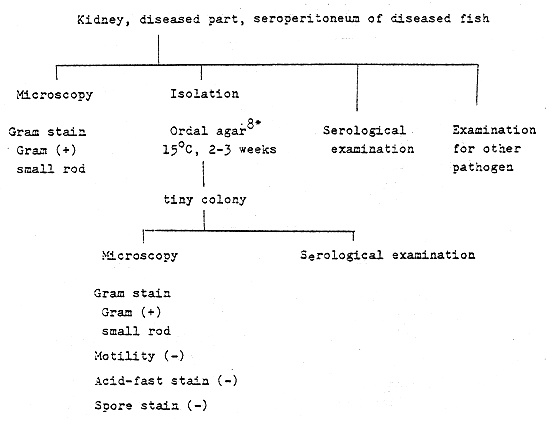
| 8*. Ordal agar | |||||
| Tryptose | 10.0g | ||||
| Beef extract | 3.0g | ||||
| Yeast extract | 0.5g | ||||
| Sodium chloride | 5.0g | ||||
| Agar | 15.0g | Distilled water | 800 ml | ||
| L-cystein hydrochloride | 1.0g | Distilled water | 160 ml | ||
| pH | 6.6 | ||||
| Human or horse serum | 40 ml | ||||
Fig. 12 - The manufacturing and immunization method of vaccines
Oral vaccine preparation (ayu)

Oral vaccine administration ( ayu)
Adsorption with vaccine on and into dryed pellet
Administration
0.1g packed cell / kg fish / day
for 10 – 14 days
Preparation

Administration
* Hyperosmotic infiltration
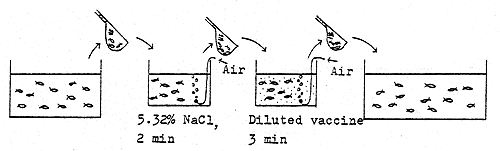
* Immersion
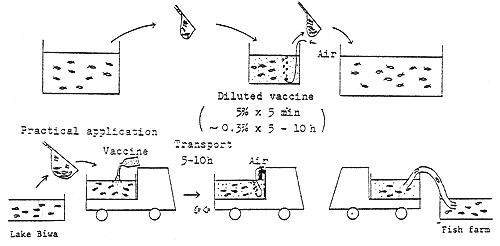
Fig. 14 - The manufacturing and immunization method of vaccines Spray vaccine preparation (ayu)
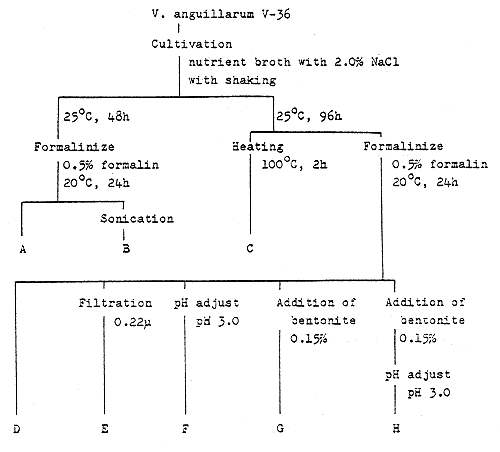
Spray administration ( ayu )
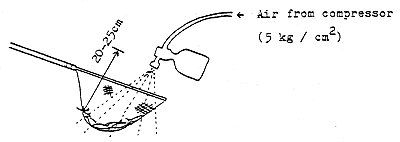
Vaccine was sprayed with spray gun for 5–7 sec at a distance of 20–25 cm from fish
Fig. 15 - The manufacturing and immunization method of vaccines
Challenging procedure 1 (ayu)
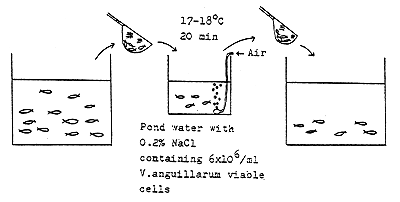
Challenging procedure 2 ( ayu )
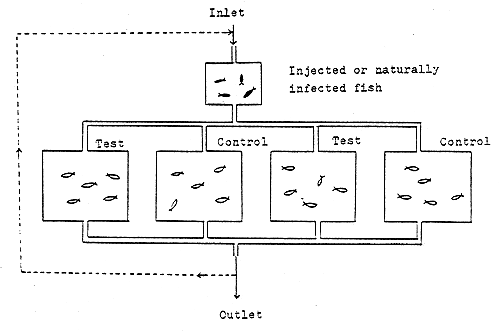
Challenging procedure