What you will learn in this module
How planning reduces risks in business management.
Demonstrating to women how they can plan their businesses.
|
SESSION PLAN |
||
|
Session 1 |
What is a business plan, why a business plan and structure of a business plan |
3 - 4 hours |
A business plan is the blueprint for implementing a business idea and the roadmap for a successful business by helping to minimize business risk.
Ask the participants how they plan before spending 500 Baht on buying clothes. As they answer, note the key words on the board or flip chart such as design, quality, colour and price. This is planning. Make the point that even an individual purchase is a result of careful consideration and link this idea with the importance of planning in the business context as given in the handout.
Explain the structure of business, highlighting each section in detail and linking this with what was covered previously in the training.
Divide the participants into groups and provide them with Business Plan formats; ask them to prepare a plan for one of the businesses of which they know the financial and technical aspects.
Hold a plenary session of the groups to find what difficulties the participants faced in preparing the business plans; explain and simplify.
Encourage participants to critique each business plan, assessing it according to the MAIR model and checking the assumptions made for the projections.
Handout 1: what is a business plan and why it is important
A business plan is a data-base of information related to the details of a business activity such as production processes, raw material, finance, support services and market.
It is important to prepare a business plan for activities at all levels. For example, if a hotel has to organize a party for 50 people, it would need to plan the menu, the material needed to make the various items, the labour required, etc., at least two to three days in advance. All the information collected about these different areas would be part of the business plan for the party.
A business plan is like a road map which makes it possible to know if the business is on the right track and monitor achievements against objectives. It helps in identifying future financing needs and is a valuable document when seeking credit and other support from bankers, government and other agencies. The business plan also helps to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the proposed business as well as the opportunities and threats it faces. This can be translated into a detailed strategy and action plan for every member of the group.
It is very important for a rural women's cooperative business to succeed. The cost of failure is very high because it undermines motivation and discourages the women from starting another other business.
Handout 2: the structure of a business plan
A business plan has the following elements:
Basic information: About the women's cooperative group such as name and address of the group. It also includes the vision and mission statement of the group.
Product/service: What is the type of business - manufacturing, service or trading? What are the products and services that will be sold?
Reasons for selecting the activity: Explain briefly why this particular business has been selected. For example, a group has decided to make baskets because a member is a skilled basket maker, there is a regular market for this product and the required raw material is available locally.
Raw material: Details about the raw material used - sources, prices, nature of availability (seasonality, if any).
What resources/supplies are needed and from where are these to be obtained? How much do these cost?
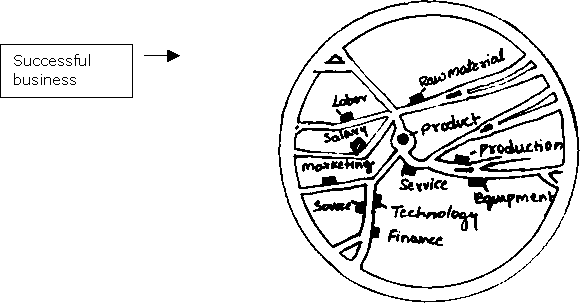
Production: Detailed information about the product, process, production requirements and cycle. For example, three months are required for making some herbal sweets. What skills are needed for production and how can these be learnt?
Personnel (division of responsibilities): Information about responsibilities of committee members. Also spells out the tasks at hand and the nature of qualified personnel who must be hired for the same.
Technology and equipment: Information on types of equipment, sources, prices, etc. What equipment is needed and where is it available?
Marketing: Information on various market channels within and outside the area, list of bulk buyers, traders, marketing cooperatives, etc. Who are the customers who will purchase/buy the product or service?
Financial aspects: Total fixed and working capital needed for the business. How much is the total cost of the business? What are the financial sources that can be accessed?
Format of a business plan
1. Basic information
|
Name of women's group: |
............................................................................... |
|
|
Address no.:............................ |
Village:.................................................................... |
|
|
Sub district:............................. |
District:................................... |
City:......................... |
|
Province:................................ |
Zip code:................................................................. |
|
|
Tel. no.:.................................. |
Fax:........................................................................ |
|
|
Name of Coop:........................................................................................................ |
||
|
Address no.:........................... |
Village.................................................................... |
|
|
Sub district:............................ |
District:................................... |
City:........................ |
|
Province:................................ |
Zip code:................................................................. |
|
|
Tel. no.:.................................. |
Fax:........................................................................ |
|
|
Total number of members: |
.............................................................................. |
|
|
Number of active members: |
.............................................................................. |
|
Vision and mission
What is the objective of forming the cooperative?
What would the group like to achieve by coming together?
2. Details about business i.e. product
Type of business (tick as applicable)
|
Production |
Service |
|
Trade |
Other |
Provide details in the table below:
|
Type product/service |
Quantity /Month |
Sales /Month |
|
No |
|
|
Name of product/service |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the advantages of the product (cheaper, better quality, unique feature, life span, etc.)?
Does the product require any government approval or need any industry standards?
3. Reasons for selecting the activity
Why you have selected this product or service?
Is it based on your skills and experience or market demand; is there any other special reason for selecting this product or service?
4. Raw material
Provide details in table below
|
Type of material |
Requirements |
|
|
|
Quantity monthly/yearly |
Total value monthly/ yearly |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Where do you obtain the above and from whom?
5. Production
What is the manufacturing cycle for each product? The entire process from the initial to the final stage must be described here. Note that if the unit makes more than one product, each must be documented individually.
How much time is required to complete the production process and put the product/s into the market?
6. Personnel (division of responsibilities)
Do you need to employ people? If yes, what type of skills do you expect the employees to have?
How will you recruit these personnel?
How much do you expect to spend on their salaries?
Details about the employees:
|
Name of the person |
Responsibilities |
Expected salary |
|
|
||
|
|
||
7. Technology and equipment
What equipment do you need? How much does it cost?
|
Machinery/ equipment |
Prices |
Numbers required |
Total value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. Marketing
Product
Who will be your customers? Clearly define your market in terms of territory and customers.
Why will they buy your products?
What type of quality measures do you intend to follow?
What type of packaging will you use?
Place (manufacturing and retail outlets)
Where will you locate your manufacturing unit and why?
Where will you locate your retail unit and why?
What expenses do you expect to incur on rental/purchase of these outlets?
Price
What are the retail and wholesale sales prices per unit?
Will customers be willing to pay the price that you have fixed? What do the competitors charge for similar products?
Have the members been consulted for end-price determination?
What will be the minimum order size and credit terms offered?
Promotion
How will you promote and distribute the product? What do you expect the promotional costs to be?
Who are your competitors? Where are they located?
What are their size and market potential? In which geographical regions are they successful currently?
What are the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors?
9. Financial aspects
A. Investment needs
What will be your financial needs? (Monthly/Yearly)
Fixed investment
Working capital
Total investment
B. Source of funds
C. Sales
What is your forecast of total sales?
Details about sales
|
Product per month |
Amount sold per unit |
Selling price per month/year |
Total sale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D. Financial statements
Profit and loss accounts as on (date)
|
Particulars (Costs) |
Amount |
Particulars (Earnings) |
Amount |
|
Opening stock |
|
Sales |
|
|
Purchases |
|
Closing stock |
|
|
Power charges |
|
Commission |
|
|
Salaries & wages |
|
Other income |
|
|
Vehicle maintenance |
|
|
|
|
Telephone charges |
|
|
|
|
Postage |
|
|
|
|
Printing and stationery |
|
|
|
|
Local conveyance/ transport |
|
|
|
|
Office expenses |
|
|
|
|
Advertisement |
|
|
|
|
Staff welfare expenses |
|
|
|
|
Accounting charges |
|
|
|
|
Professional charges (legal or other fees) |
|
|
|
|
Subscription fees |
|
|
|
|
Insurance, licenses, other permits, loan repayments |
|
|
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
|
|
Total |
A |
|
B |
|
Net Profit |
|
= B - A |
|
Profitability
Sales: (monthly/yearly)
Total costs (take from profit and loss accounts)
Gross profit = total sales - total costs
Balance sheet
What will be your balance sheet at the beginning of the business and the day of the final account-closing year (1-year)?
Starting balance sheet
|
How the money is used |
Where the money comes from (Assets) (liabilities) |
|
Cash |
Loan/grant |
|
Stocks |
Own investment |
|
Equipment |
Others |
|
Others |
|
|
Total |
Total |
Final balance sheet
|
How the money is used |
Where the money comes from (Assets) (liabilities) |
|
Cash |
Loan/grant |
|
Stocks |
Own investment |
|
Equipment |
Others |
|
Others |
|
|
Total |
Total |
Cash flow
|
Particulars |
Amount in Baht |
|||||||||||
|
Cash inflow |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
|
Opening balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales receipts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Any other income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total (A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Outflow |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electricity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Postage & telephone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Travel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repayment of loans |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Insurance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Any other expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total (B) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash flow (A-B) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Closing balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What you have learnt in this module
Business planning is the most important tool enabling the group to make a business successful. It is an aid to ensure that no aspect is neglected and the business will make profits.
The business plan must start with a statement of the cooperative's objectives and vision.
Other elements of the plan include information related to basic, technical, market, financial and personnel sectors, as well as projections for the future.
Make a Business Plan before starting a business and revise it at least once in six months, or at least once a year.