WHAT IS CONTRACT FARMING?
At the heart of contract farming (CF) lies an agreement between farmers (producers) and buyers: both agree in advance on the terms and conditions for the production and marketing of farm products. These conditions usually specify the price to be paid to the farmer, the quantity and quality of the product demanded by the buyer, and the date for delivery to buyers. In some cases the contract may also include more detailed information on how the production will be carried out or if inputs such as seeds, fertilizers and technical advice will be provided by the buyer.
Contract Farming

Recent transformations in agrifood systems have created new technical requirements and compliance costs that make it increasingly difficult for resource-poor farmers to access modern market channels. In this respect, the question of whether contract farming can be an effective institutional mechanism to address this issue stands out as one of special relevance.
The growing interest in contract farming is associated with recent transformations in food and agricultural systems which make it increasingly difficult to meet consumer demands under more traditional, open market-based procurement strategies. Demographic changes (in rapidly urbanising areas for example) and rising living standards have required increased food quantities. This increase in demand has led to scientific and technological developments, which in turn have significantly contributed to changes in market demand, the operation of supply chains and the production of raw commodities. The use of contract farming is expanding in developing countries. It opens important opportunities for economic and social development by providing local producers with access to markets and support in the form of technology transfer and credit facilities. Furthermore, contract farming is seen as a potential tool to reduce poverty, contribute to rural development and employment, and increase food security.
The purpose of this resource centre is to offer free information on contract farming in order to support a comprehensive understanding of the legal and operational aspects of contract farming for all parties involved.
Why is it important?
Contract farming has been in existence for decades. However, in recent years, its use has increased in popularity, particularly in developing countries. Globalization has brought the world closer together and the demand for food and agricultural products has increased dramatically. Food markets have become more competitive as consumers in many countries now live in cities and demand food products that are not only safe to eat, but are also produced in a way that does not damage the environment or harm the workers involved in their production. In this new context, the buyers of agricultural products need to work more closely with their partners in the supply chain so that they can source enough good quality raw materials directly from farmers to meet the demand for food products from their own customers, such as supermarkets, restaurants, hotels, schools and hospitals. Companies that process agricultural products are particularly interested in contracting with farmers, in order to secure a regular supply of raw materials that meet their needs in terms of quality and quantity.
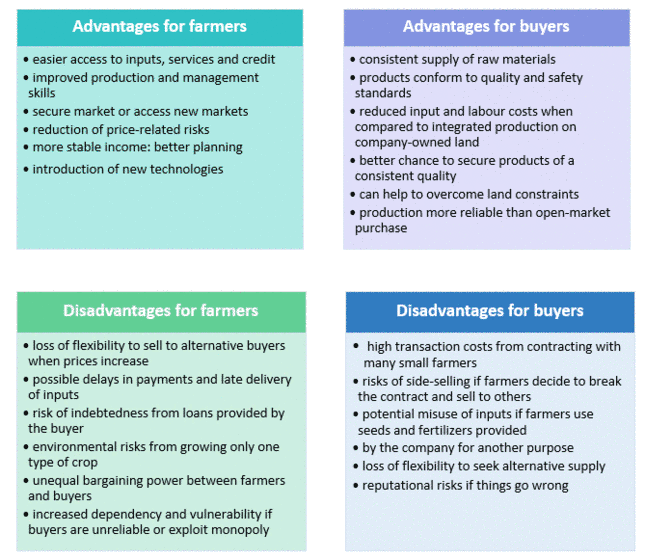
Advantages and Disadvantages
Contract farming may have advantages as well as disadvantages for both farmers and buyers, as illustrated below. However, the increase in contracting occurring around the world seems to indicate that the positive aspects tend to outweigh the negative ones.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us at [email protected].
