世界土壤日宣传材料
我们将在本页提供宣传材料,为世界土壤日造势。请经常查看本页面,因为我们将在 2023 年 12 月之前不断制作有趣的宣传材料。
传播信息!
加入#世界土壤日#活动,在网站、社交媒体等数字渠道上分享我们的宣传材料,并在您的现场活动中使用它们!
''Soil and Water: a source of life'' VIDEO
OFFICIAL POSTER | OFFICIAL WORLD SOIL DAY CARDS | MEGABANNERS | WEB BANNER | T-SHIRTS | VIRTUAL BACKGROUND & TEMPLATE FOR PRESENTATIONS | SOCIAL MEDIA CARDS | EDUCATIONAL POSTERS | COMICS | LOGOS | VIDEOS | POSTER SERIES | POSTCARDS | THEMATIC INFOGRAPHICS | THEMATIC FACTSHEETS
World Soil Day, 5 December 2023 | OFFICIAL POSTERS
World Soil Day, 5 December 2023 | OFFICIAL WORLD SOIL DAY CARDS
World Soil Day, 5 December 2023 | MEGABANNERS
World Soil Day, 5 December 2023 | WEB BANNERS
The World Soil Day 2023 Web Banners can be downloaded here:
Georgian: Square 220x220px, Square 426x426px, Rectangular 460x213px, Rectangular 920x426px.
Persian: Square 220x220px, Square 426x426px, Rectangular 460x213px, Rectangular 920x426px.
Portuguese: Square 426x426px, Rectangular 920x426px.
World Soil Day, 5 December 2023 | T-SHIRTS
Giving out T-shirts at WSD events can create real team spirit and gives everyone involved a nice souvenir of the day.
With these files, you can print your own WSD t-shirts. It’s not hard. We’ve provided the instructions.
Arabic | Chinese | English | French | Russian | Spanish
World Soil Day, 5 December 2022 | VIRTUAL BACKGROUND
Are you conducting and/or participating to a virtual event for World Soil Day? Use our virtual background!
World Soil Day, 5 December 2023 | PPT PRESENTATION
Do you need to deliver a presentation for World Soil Day? You can download the official WSD template: ENGLISH
World Soil Day, 5 December 2023 | NEW SOCIAL MEDIA CARDS
Global Soil Doctors Programme | EDUCATIONAL POSTERS ON SOIL AND WATER
Discover the all series: Soil Doctor Educational Poster
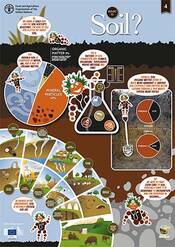
What is soil?Soils are complex mixtures of minerals, water, air, organic matter, and countless organisms that together support life on Earth. Download PDF: High res Official languages: French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic Other languages Chichewa; Chewa; Nyanja | Dioula | Fulah | Kazakh | Lao | Mossi | Tumbuka | Bengali | |
What is soil erosion?This poster explains what soil erosion is. Official languages: English | French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic Other languages: Kazakh
| |
How to best minimize soil erosion by water?This poster explains how to minimize soil erosion by water. Official languages: English | French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic Other languages: Dioula | Fulah | Mossi
|
World Soil Day logo
The official WSD logo is available for download and use to help the campaign at your event! Look out for more languages in the coming weeks! If you would like to request the logo in a new language, please send an email to [email protected].
EN: S | M | L | pdf FR: S | M | L | pdf ES: S | M | L | pdf RU: S | M | L | pdf AR: S | M | L | pdf CH: S | M | L | pdf
All translations are available on the WSD logo webpage!
视频
6 actions to keep soil alive
|
Soil organisms are essential for food security, climate change and the environment. An agenda for action on soil biodiversity is needed to protect, strengthen monitoring, and prevent further biodiversity loss. |
Beneath our feet
|
World Soil Day - Keep soil alive, Protect soil biodiversity, focuses on soil biodiversity as a key factor to achieve food security, mitigate climate change and improve human health. |
Keep soil alive, protect soil biodiversity
|
Keep soil alive, protect soil biodiversity This animation gives a brief introduction on the main drivers, the key functions and challenges of soil biodiversity loss, indicating possible ways to enhance soil biodiversity as a nature-based solution. English | عربية | 中文 | Français | Pусский | Español | Thai | Portuguese | Italian Short version: English |
Mission: Keep soil alive!
|
Soils are essential for food systems. Healthy soils allow us to grow a variety of food products needed for human nutrition and each of us depends on soil productivity. |
Stop soil erosion, Keep soil where it belongs
|
Stop soil erosion, Keep soil where it belongs Soil erosion poses a major threat to global food security and to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Find out more about the effects of soil erosion and the ways we can prevent it. |
Soil Pollution: a Hidden Reality
|
Soil Pollution, a hidden reality Soil is a complex growing habitat that remains productive only when it is cared for and nurtured. Combating and addressing soil pollution means assessing and minimizing the risks for food security, human health and the environment. |
The Global Soil Organic Carbon Map V1.0
|
The Global Soil Organic Carbon Map V1.0 The Global Soil Organic Carbon map V1.0 is an important stepping stone to better know the current Soil Organic Carbon stock stored beneath our feet and soils’ potential for further sequestration. |
Soil Organic Carbon
|
Soil organic carbon, the treasure beneath our feet An animated illustration of soil organic carbon and its importance for climate action, food production and sustainable development. |
Soils and Pulses
|
Soils and Pulses, Symbiosis for Life This short animation introduces the new book “Soils and Pulses: symbiosis for life”. Pulses contribute to soil health, food security and nutrition, and climate change adaptation and mitigation. |
Soil and SDG's
|
Sustainable soil management and the Sustainable Development Goals The Sustainable Development Goals were recently created with a view to achieve sustainable development by 2030. Of the 17 goals, four contain targets specifically related to Soils. This animation looks at some of the challenges we face in each of these goals and presents some of the methods we can use to tackle them. |
Soil and Nutrition
|
Soil: An essential ingredient to healthy food and nutrition Soils are by nature linked to the micronutrient content of our food production and they can help to reverse the increasing trend of nutrient depleted soil by adopting sustainable soil management practices. |
Soil and Climate change
|
Soils: Our ally against climate change A look at how our Soils help to combat climate change in their role of sequestering CO2, and how our collective habits can damage this benefit with potentially devastating consequences. |
Soil 101
|
Soil 101 is an animated introduction on soils prepared in the framework of the 2015 International Year of Soils. This 2 minutes video outlines the main soil functions and the threats currently facing them. English | العربية | 中文 | Français | Pусский | Español | čeština | |
Soil: Limited natural resource
|
Soils are a limited natural resource, but their role in food security is crucial. In light of climate change, soil degradation and erosion, farmers struggle to protect soil health. |
Infographics
Soil biodiversity, the hidden world beneath our feet
This infographic aims to raise awareness on soils biodiversity that represents the hidden world beneath our feet.
Arabic | Chinese | English | French | Russian | Spanish
Other languages: Catalan | Portuguese | Slovenian
Soils and the SDGs
This infographic aims to raise awareness on soils and link healthy soils have with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Aboveground and belowground biodiversity: an inseparable interaction
The interaction between below and aboveground biodiversity, including several different animals, plants and bacteria that are part of this symbiotic relationship.

Soil pollution and phytoremediation
Some plants can uptake, remove and stabilize contaminants from the soil, through different mechanisms.
Impacts of soil pollution on key soil functions
Soil pollution causes a chain of degradation processes in soil, jeopardizing its ability to provide ecosystem services.
Pollution-induced changes in the functioning of soil ecosystems
Mobile soil fauna often uses an avoidance strategy, reducing the first steps of litter decomposition in heavily polluted soils.
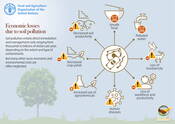
Economic losses due to soil pollution
Soil pollution entails direct remediation and management costs ranging from thousands to billions of dollars per year, depending on the extent and type of contaminants.
Soil pollution jeopardizes the achievement of most of the SDGs
The prevention, control, and remediation of soil pollution are fundamental if we want to implement the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
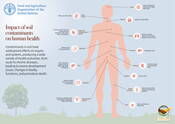
Impact of soil contaminants on human health
Contaminants in soil have widespread effects on organs and systems, producing a wide variety of health outcomes, from acute to chronic diseases, leading to severe development issues, changes in bodily functions, and premature death.
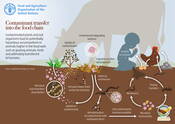
Contaminants tranfer to the food chain
Contaminated plants and soil organisms lead to potentially hazardous accumulations in animals higher in the food web such as grazing animals, birds and ultimately transferred to humans.
Soil pollution, a hidden reality
This poster presents in a nutshell the sources, degradation processes and effects of soil pollution on the environment, human health and food safety and security.
Other languages: Thai
Soil pollution is borderless
Soil pollution is a borderless often invisible threat whose presence and effects are present in every corner of the globe.
 Soil pollution, a hidden reality
Soil pollution, a hidden reality
This poster presents in a nutshell the sources, degradation processes and effects of soil pollution on the environment, human health and food safety and security.
Soils and pulses , symbiosis for life
The symbiotic and strategic alliance between soils and pulses contributes to improve soil health, adapt to and mitigate climate change, and ultimately to enhance food security and nutrition.
Soils are key to unlocking the potential of mitigating and adapting to a changing climate.
English | Français | Русский | العربية | 中文 | Español | Deutsch | Georgian | Catalan
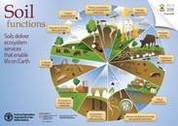
Soils deliver 11 key ecosystem services that enable life on Earth.
العربية | 中文 | English | Français | Русский | Español | Turkish | Deutsch | Hungarian | Dutch/Flemish | Thai | Georgian | Slovenian | Catalan | Italian | Portuguese | Finnish | Czeck | Swedish

Soil an essential ingredient to healthy food and nutrition
Soils are by nature linked to the micronutrient content of our food production. Sustainable soil management can help to reverse the increasing trend of nutrient depleted soil.
English | Turkish | Deutsch | Georgian | Spanish

Soils are under increasing pressure of intensification and competing uses for cropping, forestry, pasture, urbanization. These, combined with unsustainable land uses/management, as well as climate extremes, cause degradation.
العربية | 中文 | English | Français | Русский | Español | Turkish | Deutsch | Thai | Georgian | Catalan

Formation of soil is a complex and long process which depends on 5 key formation factors. Soils around the world are very diverse and constitute a key element of our landscapes
العربية | 中文 | English | Français | Русский | Español | Czech | Finnish | Swedish | Deutsch | Thai | Georgian | Catalan

Healthy soils not only are the foundation for food, fuel, fibre and medical products, but they are also playing a key role in the carbon cycle, storing and filtering water, and improving resilience to floods and droughts.
العربية | 中文 | English | Français | Italiano | Русский | Portouguese | Español
The official posters to celebrate World Soil Day are available for download and print to help the campaign !
|
| |
|
|
|
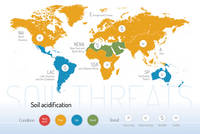
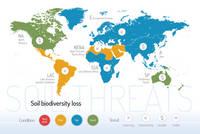
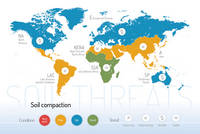
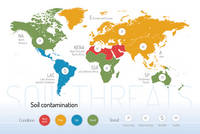
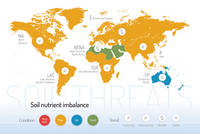
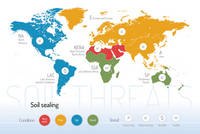
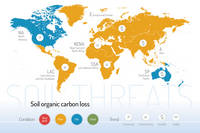
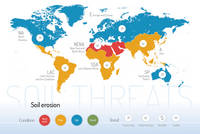
Threats on soil functions
A series of 9 postcards focusing on the main soil threats have been produced together with a world map showing the condition and trend of each specific threat worldwide.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Soil salinization and sodification | ||
|
| |
|
|
|
Thematic infographics

Soils store and filter water - Improving food security and our resilience to floods and droughts
Functional soils play a key role in the supply of clean water and resilience to floods and droughts.

Soils help to combat and adapt to climate change
Soils help to combat and adapt to climate change by playing a key role in the carbon cycle.

Soils are the foundation for vegetation
Healthy soils are crucial for ensuring the continued growth of natural and managed vegetation, providing feed, fibre, fuel, medicinal products and other ecosystem services such as climate regulation and oxygen production. Soils and vegetation have a reciprocal relationship.

Soils and Biodiversity
Soils host a quarter of our planet's biodiversity.Soil is one of nature's most complex ecosystems: it contains a myriad of organisms which interact and contribute to the global cycles that make all life possible.
French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic Other languages: Hungarian

Healthy Soils are the Basis for Healthy Food Production
Healthy soils produce healthy crops that in turn nourish people and animals. Indeed, soil quality is directly linked to food quality and quantity.
French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic Other languages: Turkish | Italian

Soil is a non-renewable resource. Its preservation is essential for food security and our sustainable future
Soil is a finite resource, meaning its loss and degradation is not recoverable within a human lifespan.
French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic Other languages: Hungarian | Turkish | Italian | Indonesian

International Year of Soils 2015: Healthy soils for a healthy life (available soon)
Our soils are in danger because of expanding cities, deforestation, unsustainable land use and management practices, pollution, overgrazing and climate change.
French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic Other languages:
Thematic factsheets

Soils store and filter water
Improving food security and our resilience to floods and droughts
Functional soils play a key role in the supply of clean water and resilience to floods and droughts. Water infiltration through soil traps pollutants and prevents them from leaching into the groundwater. Moreover, the soil captures and stores water, making it available for absorption by crops, and thus minimizing surface evaporation and maximizing water use efficiency and productivity
Download PDF: High res | Low res
Official languages: French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic
Other languages

Soils help to combat and adapt to climate change by playing a key role in the carbon cycle
Healthy soils provide the largest store of terrestrial carbon. When managed sustainably, soils can play an important role in climate change mitigation by storing carbon (carbon sequestration) and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions in the atmosphere.
Download PDF: High res | Low res
Official languages: French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic
Other languages

Soils are the foundation for vegetation
which is cultivated or managed for feed, fibre, fuel and medicinal products
Healthy soils are crucial for ensuring the continued growth of natural and managed vegetation, providing feed, fibre, fuel, medicinal products and other ecosystem services such as climate regulation and oxygen production.
Download PDF: High res | Low res
Official languages: French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic
Other languages

A healthy soil is a living soil
Soils Host a Quarter of our Planet’s Biodiversity
Biological diversity or ‘biodiversity’ is described as “the variability among living organisms from all sources, whether terrestrial, aquatic or marine”. It includes the diversity within species (genetic diversity), between species (organism diversity) and of ecosystems (ecological diversity)...
Download PDF: High res | Low res
Official languages: French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic
Other languages

Healthy soils are the basis for healthy food production
The most widely recognized function of soil is its support for food production
It is the foundation for agriculture and the medium in which nearly all food-producing plants grow. In fact, it is estimated that 95% of our food is directly or indirectly produced on our soils. Healthy soils supply the essential nutrients, water, oxygen and root support that our food-producing plants need to grow and flourish. Soils also serve as a buffer to protect delicate plant roots...
Download PDF: High res | Low res
Official languages: French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic
Other languages

Soil is a non-renewable resource
Its preservation is essential for food security and our sustainable future
Soil is a finite resource, meaning its loss and degradation is not recoverable within a human lifespan. As a core component of land resources, agricultural development and ecological sustainability, it is the basis for food,feed, fuel and fibre production and for many critical ecosystem services. It is therefore a highly valuable natural resource, yet it is often overlooked...
Download PDF: High res | Low res
Official languages: French | Spanish | Chinese | Russian | Arabic
Other languages
World Soil Day, 5 December | COMICS
当添加任何世界土壤日材料到你的网页,请记着链接这些材料到网址 www.fao.org/world-soil-day/en/