Appendix A - Preparing support materials
Appendix B - Some common games
Appendix C - Visual support materials available in the region
Appendix D - Organizations with which linkages can be established
Preparing Support Materials for Non-Formal Population Education
Generally, the intensive and diversified use of support materials for the non formal population education is crucial in view of the adverse realities, some of which arc given below:
* Almost one third of the world's adult population cannot read and write.
* Women compose 60% of this population and the number is increasing.
* It is important to reach out to this non-reading, non-writing women population because they are precisely the vulnerable group and are most in need of population education.
There is an old Chinese adage which goes:
IF I HEAR IT, I FORGET IT
IF I SEE IT, I REMEMBER IT
IF I DO IT, I KNOW IT.
* Unfortunately, not all of our teaching methods and our resources will be able to cater to the "on the job" training type of education. For bigger audiences and for wider reach, we need to have group teaching methods that rely heavily on the use of visual support materials.
* There are various types of visual support materials that have been proven effective in population education. These materials include flip charts, flash cards, leaflets, comic books and magazines. Lately, there has been much use for visuals silk-screened in rough chambray or cheesecloth
Advantages/Disadvantages of Each Type of Visual Support Material
In selecting the type of visual support materials for our NFPE activities, it would be helpful to know the strengths, as well as the limits, of the materials we arc planning to use:
* Flip Charts
Advantages:
+ Convenient to use because the concepts needed to be explained are already prepared.
+ Drawings can be put together so that they can be arranged in the order the topic will be discussed.
+ Flip charts made from cloth have been found to be of popular use because they can be folded or rolled and can be easily carried. Unlike chants made of cartolina or cardboard/illustration board, flip charts made from cloth do not get easily damaged when wet.
Figure
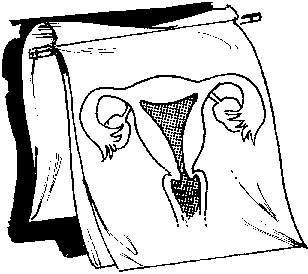
Limitations:
- Flip charts can only be used for an audience of not more than 25 persons. Otherwise, these will not be seen? especially by those located far from where the charts are shown.
- Since the illustrations in the charts do not show much movement and have to be simplified for visual impact, there is still the need for an effective verbal enrichment/explanation of the concepts presented.
* Flash Cards
Advantages:
+ Flash cards are easy to carry. More concepts can be introduced in several cards which can show progress or movements.
+ They can be easily developed, and the audience can even participate in making some of the cants.
Limitations:
- Flash cards can only be used for smaller groups of not more than 15 persons. However, they are best used for home visits or for face-to-face sessions.
- The smaller size of the flash cards somehow diminishes the impact of the presentation and is not as dramatic as, say, the flip chart.
Figure
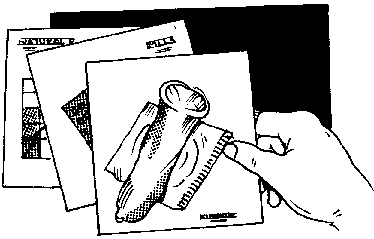
* Leaflets
Advantages:
+ Messages can reach a larger number of people, limited only by the supply of leaflets and the people who will do the distribution. This has multiplier effect because the material can be passed on to others after the first set of audience has studied them.
+ The readers get to retain their copy of the messages which they can review when needed. In some instances, the leaflets are even used as wall posters, as a constant reminder of what needs to be done. This is specially useful when using such contraceptives as the pill because the mother gets a constant reminder that she should take the contraceptive.
Limitations:
- No matter how well-illustrated the leaflets are, the audience must still know how to read because not all the messages can be contained in the illustrations. This limits the audience to those who are literate, unless somebody can read the literature to them.
- Producing leaflets would entail a bigger amount of initial expenses for printing and even for conceptual development. The smaller the print run, the more expensive is each individual copy.
Figure
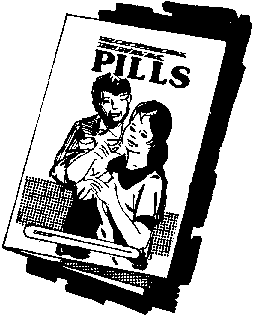
* Comics
Advantages:
+ This is a favorite form of entertainment in the rural areas, where the audience is already familiar with the comics.
+ This can be distributed to as big an audience as the budget would allow.
+ More messages can be incorporated in story form. The material can be read by the audience over and over again and can be passed on to others who are interested, or who may need to read them.
Figure
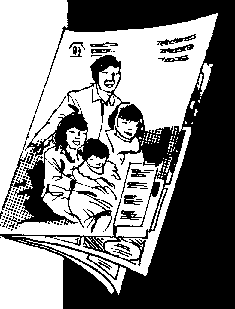
Limitations:
- Comics entail more funds than the preparation of the leaflets. A skilled artist and writer should develop the concepts in population education in such a way that they not look like they are forced within the story.
- The audience is limited to those who have a medium level of literacy. That is, their reading skills are not as developed as, say, someone who has gone through four years of elementary education.
Figure
TIPS IN PREPARING VISUAL MATERIALS
* Layout
- Visual aids must be easily legible. If there are letterings to be done, they must at least be two inches in height if they are to be easily seen by the audience. it is difficult to read this........
Figure 1

Figure 2

THIS IS CLEAR AND EASY TO READ
Figure

- The visual aid must be clean and neat.
Figure

- Present one message for every illustration.
Figure

- Limit the number of concepts/pages for each material so as not to bore/overload the audience.
Figure
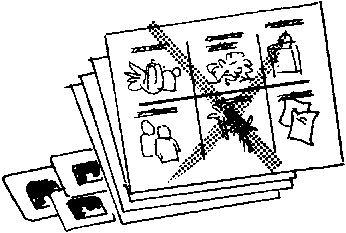
- Leave plenty of white space so that the material can be easily understood and will not look crowded.
Figure
- Arrange messages in sequence that is most logical to the audience. We should consider that people usually read from left to right and from top to bottom.
Figure
- Use illustration to supplement text.
Figure

* Illustrations
- Use familiar images or representations. People can easily understand and associate things that are familiar to them.
Figure

- Use simple line drawings so that the audience will not be distracted from the main message.
Figure
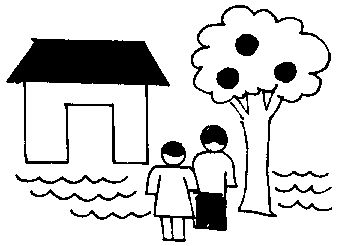
- Use a positive approach. Negative approaches might be discouraging.
Figure
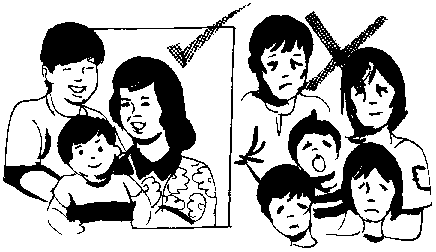
- As much as possible, make illustrations that encourage analytical skills and allow discovery.
Figure
SOME COMMON GAMES THAT CAN BE USED FOR NON-FORMAL POPULATION EDUCATION
1. Rumor Clinic
* Before starting the game, decide on the messages that you want to relay. The following are sample messages:
- Breastfeeding is best for your baby.
- Small families, happy families.
- Women power, people power.
You can make your own messages which are suited or relevant to the conditions of your area/audience.
* Ask the participants to form 3 lines of around 10 persons each. Select a Game Watcher for each line.
* The message is whispered by the Game Watcher to the person in front of the line. The person in front then whispers the message to the next to her or him, and so on, until this reaches the person at the end of the line. The latter then runs forward and whispers the message to the Game Watcher. The first group who gives the correct message gets 1 point.
* The group who gets the most number of points win the game.
2. Tic- Tac - Toe
* Materials needed:
Blackboard
Chalk
Questions in index card
* Divide the participants into 2 groups. One group will take the "X" sign, while the other will take the "O" sign.
* Draw the diagram below on the board, big enough for everybody to see.
Figure

* From a set of prepared questions, draw one question at a time.
Example:
What is the ideal number of children per family?
The group who answers "2" (the correct answer) first gets to put their sign on the board.
If the answer given by the first group is wrong, the second group is given the chance to answer the question.
If both answers are wrong, the Game Master gives the right answer with some explanation, and goes to the next question.
* The first group who draws a straight line using their sign (examples shown below), wins the game.
Figure
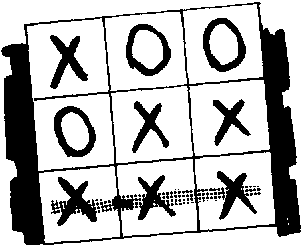
3. Snakes and Ladders
* Materials needed:
Game board
Dice
Marker
* The object of this game is to reach a designated point on the board, which represents success.
* You can make a board out of a cardboard folder or cartolina as shown below:
Figure
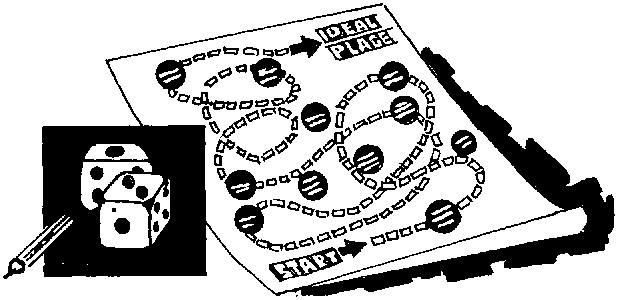
* You can divide the participants into groups of 5. Each group shall be given a gameboard, a die, and one marker for each participant.
* The participants take turns in rolling the die.
* Beginning in the spaced marked "start", the player counts the spaces shown in the die. If the player falls on a "positive" space, he or she advances. Positive spaces are those which show desirable values. For example, if the marker falls on a space which shows women and men helping each other do the housework, the player advances to some spaces, or gets another turn in rolling die. "Negative" space are those which show undesirable values, such as women not included in community meetings. If the player falls in the space, he or she either goes back some spaces, or loses a turn.
* The first player to reach the "ideal place" or the goal, wins.
4. Family Feud
* Materials needed:
Brown paper/kraft paper
Blackboard
Chalk or marker pens
Questions (to mark on kraft paper) on index cards
* The object of the game is for a team to win as many points as possible.
* The participants shall be divided into two-groups. Each group will select a leader.
* On the board, or brown paper, you can draw a figure showing the first letters of the answers to the questions. The first letters can themselves form a message as shown below:
* The Game Master can start with the first letter and ask:
What "W" is said by the Chinese to "hold half the sky?"
Answer: Women
* Then he or she goes to the next letter:
What "O" prevents dehydration?
Answer Oresol (or oral rehydration solution)
* The Game Master goes on until he or she completes all the letters.
* In case the players cannot answer the question, and the Game Master has to give the answer, he must have a back-up question(s) for the same letter.
* It should be noted that in cases where the participants do not know the answer, the Game Master should provide more details regarding the correct answer. In this way, the participants are further educated.
5. The fertility game
Materials:
* Questions
* Stock of cards showing contraceptive method, and corresponding points
Instructions:
* Divide the participants into 2 groups
* Ask them to line up.
* The 2 in front will be asked a question. For example: What contraceptive method is contraindicated for women who have heart problems? Answer: pills
* The first one who gives the correct answer will be asked to draw a card. Each card will have a corresponding point, with the explanation:
- Pills - If taken appropriately, this has a 97% effectiveness. You score 5 points.
- Billings' method - This method may not be as reliable because changes in body secretion are sometimes not discerned rightly. You score 2 points.
* After the participants in front of the line have finished with their turn, they move to the back of the line.
* Each group will then total the number of points that they have made.
* The group with the most number of points wins the game.
* The facilitator will make a synthesis of the session by relating the use of more effective family planning methods to peace of mind, to less number of children, and eventually to the improvement of the quality of life of the family.
LIST OF VISUAL SUPPORT MATERIALS FOR NON-FORMAL POPULATION EDUCATION AVAILABLE IN SOME PARTS OF THE REGION
1. Communication Foundation for Asia Sta. Mesa, Manila, Philippines
Title : Population and Sex Education
Target Audience: Out-of-School Youth, Premarriage Couples, Post-Natal Mothers
This is a 7"x19" 68-page comic book printed on newsprint.
The comic book touches on sexual awareness and responsibility in the face of overpopulation and focuses on population growth and its consequences.
2. Commission on Population Welfareville Compound, Mandaluyong, Metro Manila Philippines
Title : Sa Aking Pagkatao (About My Personality)
Target Audience: Youth
This slide-tape-presentation focuses on sex education for the youth. Running time: 25 mins.
Title : Sex and the Child
Target Audience: Parents
This 16 mm film features what children know about human sexuality, how parents perceive what they know about these things, and what they teach their children.
3. Philippine Center for Population and Development Pasong Tamo Extension Taguig, Metro Manila
Title : Three Friends... Three Experiences
Target Audience: General
This slide-tape-presentation deals with the consequences of abortion and early pregnancy. It also shows the advantages and disadvantages of delaying marriage.
Title : Planning Your Family the Natural Way
Target Audience: Married Couples of Reproductive Age
This is an instructional slide-tape presentation on 3 natural family planning methods: sympto-thermal, basal body temperature and calendar rythm.
Figure
ORGANIZATIONS WITH WHICH LINKAGES CAN BE ESTABLISHED
A. Women's Desk: c/o ESCAP, United Nations Building, 1 Rajdamnern Avenue, Bangkok 2, Thailand.
B. Asia and Pacific Centre for Women and Development
(APCWD) c/o Asia and Pacific Development Centre (APDC), P.O. Box 2224, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Objective:
To ensure the full participation of women in the economic and social development of their communities.
Activities:
The provision of technical and advisory services to governments, non-governmental organizations and UN Specialized Agencies, to assist in the development of programmes and projects from which women will benefit; skills-training courses; research and case studies; preparation of training manuals; establishment of networks of technical support and information exchange among women and women's groups, and with governmental, national and international sources of aid to women.
Aims:
To enhance the role of Asian women in the economic, cultural and spiritual development of the region, and increase their participation in world affairs; to help Asian women gain access to educational and cultural activities; to promote human welfare and defend human rights
The Forum was initiated in order to share experiences and ideas and to build a network through which to develop cooperative programmes of action. Through the Forum, women can seek assistance from others regarding approaches to problems they may meet in the course of working towards improving the lives of women in their country.
C. Women in Adult and Non-Formal Education
International Council for Adult Education
29 Prince Arthur Avenue
Toronto, Ontario M5R 1B2, Canada
D. Network of Women in Development Resource Centres
International Women's Tribune Center, Inc.
305 East 46th Street, 6th Floor
New York, NY 10017 USA
E. Women's Network for Population and Development
c/o Peggy Curlin
The Centre for Population Activities
1717 Massachusetts Ave., N.W.
Suit 202
Washington, D.C. 20036
F. Indonesia's Office of the State Minister for the Role of Women
Ministry for the Role of Women
Medan Merdeka Barat 15
Jakarta 10110
Indonesia
G. Malaysia's Women's Affair's Division
Ministry of National Unity and Social Development
14th Floor, Wisma Shen
Jalan Masjid India
50562 Kuala Lumpur
Malaysia
H. Thailand's Office of the National Commission in Women's Affair's
Office of the Permanent Secretary
Office of the Prime Minister
Government House
1 Phitsanuloke Road, Rusit
Bangkok 10300
Thailand