Project list
FAO implements a wide range of development and emergency assistance projects in Pakistan. Projects are funded by organization’s own funds, bilateral and multilateral aid agencies, and governments including the Government of Pakistan. Below is the list of currently implemented projects grouped by the type of funding.
Reversing Deforestation and Degradation in High Conservation Value Chilghoza Pine Forests in Pakistan

Chilghoza forests occur in the dry temperate zone of Pakistan and hold tremendous importance from both ecological and economical perspectives. However, these forests are under tremendous pressure due to demand surpassing their capacity. The project is part of “The Restoration Initiative” aimed at improving local livelihoods by enhancing productivity and services in the chilghoza forests of Pakistan. The project is implemented in the Sherani district of Balochistan, South Waziristan and Chitral districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Diamer district of Gilgit-Baltistan. Through active participation of the local communities, the project aims to bring approximately 30 000 hectares of chilghoza forests under sustainable forest management. In addition to local benefits, the project is also contributing to global environmental benefits by mitigating an estimated amount of greenhouse gas emissions.
This four years project is being implemented with stakeholders from the national, provincial, and district levels playing an integral role in the implementation of project interventions. The project and all associated activities are being executed in the target provinces through the Direct Execution (DEX) modality, with FAO serving as the Global Environment Fund (GEF) agency.
Key activities under this project include establishing 14 community forest protection conservation committees; developing chilghoza multi-functional plans; valuing chilghoza forest production, services, and functions; introducing payment for ecosystems (PES); sustainably managing 30 000 ha of chilghoza forests; restoring 4 400 ha of forest area and improving 3 600 ha; establishing agroforestry community plantations on 1 000 ha; distributing fruit and forest plants for agroforestry; providing necessary tools and equipment such as chilghoza harvesting tool kits. 7 chilghoza processing units (consisting of Grading Machine, Washer, Dryer, Roaster and Packing machines) are installed in targeted valleys. Four community training resource centers (one in each targeted region) are under completion.
Resource Partner(s) | Global Environment Fund (GEF) Provincial Forest Departments of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (South Waziristan and Chitral), Balochistan (Sherani), and Gilgit-Baltistan (Diamer)
|
Budget | USD 3 978 440
|
Duration | Six Years and Two Months April 2018 – June 2024
|
Geographic Coverage | The project activities will cover four key dry temperate Chilghoza forest sites: Balochistan: Suleiman Mountain Range Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Shishi-valley of Chitral South-Waziristan: Suleiman Mountain Range Gilgit-Baltistan: Diamer District
|
Beneficiaries | 50 000 Households
|
Implementing Partner(s) | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Ministry of Climate Change Women’s Organizations Forest Conservation and Protection Committees
|
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of Climate Change Provincial Forest Departments of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (South Waziristan and Chitral), Balochistan (Sherani), and Gilgit-Baltistan (Diamer)
|
Support to SDGs
Capacity Building on the Sustainable Conservation and Utilization of Medicinal Plants and Non-Timber Forest Products in Astore Valley and Deosai National Park Buffer Zone of Gilgit-Baltistan

The project is being implemented in the Astore valley and the adjoining buffer zones of Deosai National Park (DNP) due to its rich biodiversity and the presence of globally significant species of fauna and flora. The prime objective of the project is to promote the in-situ conservation and sustainable use of medicinal plants and other non-timber forest products (NTFPs) in the target area. This is done through ethnobotanical surveys aimed at assessing the utilization, distribution, status, and volume of harvested medicinal plants. The project also is to identify and implement appropriate management options to ensure sustainable harvesting of medicinal plants and other NTFPs. Another important aspect is to enhance the capacity of the local community in sustainable harvesting of medicinal plants.
FAO Pakistan is implementing the project in close collaboration with the Forest, Parks, and Wildlife Department of the Government of Gilgit-Baltistan. Under the Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP), FAO is contributing its technical expertise with those of other partners to ensure a holistic and perspective approach.
The expected outcome of the project is the assessment and enhancement of the conservation and utilization of medicinal plants, NTFPs, and other habitats in Astore Valley and the Deosai National Park buffer zone of Gilgit-Baltistan.
Resource Partner(s) | Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP)
|
Budget | USD 100 000
|
Duration | Two Years December 2022 – November 2024
|
Geographic Coverage | Gilgit-Baltistan: Astore Valley and Deosai National Park Buffer Zone |
Beneficiaries | 400 Households
|
Implementing Partner(s) | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Ministry of Climate Change Forest, Parks and Wildlife Department, Government of Gilgit-Baltistan Local community organizations
|
Government Partner(s) | Forest, Parks and Wildlife Department, Government of Gilgit-Baltistan
|
Support to SDGs
Implementation of Codex Standards to Support Containment and Reduction of Foodborne Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)

Pakistan is actively participating in the 5-year "Action to Support the Implementation of Codex AMR Texts" (ACT) project, which is a part of a global initiative. The primary goal of this project is to promote the responsible and judicious use of antimicrobials to combat the proliferation of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). This initiative specifically targets the reduction of AMR in the realm of food safety by advocating for the implementation of guidelines outlined in the Codex Alimentarius (Food Code). The Codex Alimentarius serves as a comprehensive framework, delineating the necessary measures and policies for safeguarding consumer health and ensuring equitable practices within the food industry.
The project employs a three-pronged strategy, collaborating with various AMR stakeholders including government ministries, veterinarians, farmers, and others. Firstly, it strives to heighten awareness about AMR across both the public and private sectors involved in food production. Secondly, it provides support to enhance the capabilities of food safety laboratories in detecting AMR in food samples. Finally, the project engages with government authorities to encourage the widespread adoption of the recommended best practices detailed in the Codex Alimentarius
Pakistan's experiences and insights gained from this initiative are actively shared with other nations, demonstrating effective strategies for enhancing food safety. Simultaneously, the adoption of these strategies contributes to the preservation of the efficacy of essential drugs in combating infections.
Resource Partner(s) | Republic of Korea |
Budget | USD 1.67 million (For Pakistan) |
Duration | 5 Years |
Geographic Coverage | Pakistan |
Beneficiaries | Livestock farmers, Federal and Provincial Livestock and Dairy Development Departments, Food authorities, Federal and Provincial Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratories, Veterinary Professionals, Consumers and Students. |
Implementing Partner(s) | FAO is directly implementing the project |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security & Research |
Support to SDGs
Building Capacities on Food Systems with a Special Focus on Gender and Women Empowerment

The agriculture sector is a key driver of Pakistan's economic growth and plays a crucial role in ensuring food security for its population. However, this sector currently faces various challenges that hinder its potential for growth and sustainability. This TCP project aims at supporting the Government of Pakistan in transforming its food systems, with a specific focus on women, gender, and development. Women play a significant role in agriculture but face challenges in terms of resource ownership, access to services, and decision-making. It is essential to address the gaps in the food system and promote gender-sensitive value chain development to achieve gender equality and improve food security.
The project is being implemented in close collaboration with its government counterpart, the Ministry of National Food Security and Research. It involves policy dialogues, capacity-building activities, technical assistance, and coordination with relevant stakeholders.
The project has completed the following outputs:
- A Global Action Plan (GAP) framework implementation strategy developed with women-specific action.
- Supported the Government of Pakistan for the Food Systems Summit 2021.
- Developed a cluster farming strategy and implemented plan with targeted actions for women farmers.
- Reviewed agriculture commodity price policy and legislation in Pakistan.
- Developed a strategy for emergency and resilience work in the agriculture sector of Pakistan, addressing gender gap and protection issues.
- Reviewed food safety situation in Pakistan.
- Strengthened technical capacities of government staff in estimation and interpretation of SDG indicators.
- Studies conducted on food System and rural transformation.
- A study on feasible linkages between poverty graduation programmes, inclusive rural development, sustainable agriculture, and food and nutrition (in progress).
- A study on National Poverty Graduation Programme (NPGP) time allocation analysis (in progress).
- A study on development and feasibility assessment of village social enterprise models (in progress).
It is expected that the project will result in enhanced Food and Nutrition Security in Pakistan and strengthened capacity of the Ministry of National Food Security and Research in food systems approaches and policies with a special focus on women.
Resource Partner(s) | Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP) |
Budget | USD 378 000 |
Duration | 32 Months |
Geographic Coverage | Pakistan, National |
Beneficiaries | Ministry of National Food Security and Research and Provincial Line Ministries |
Implementing Partner(s) | N/A |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research (MNFS&R) |
Support to SDGs
Transforming the Indus Basin with Climate Resilient Agriculture and Water Management

Climate change poses significant threats to the future livelihoods of farmers and the agriculture sector around the Indus Basin in Pakistan. The project was designed to address climate challenges by departing from the "business as usual" approach in the Indus Basin. It aims to increase resilience to climate change among the most vulnerable farming community in the Indus Basin and to strengthen public/private sector capacity for the development of climate-smart agriculture. The project is achieving its objectives through:
Establishing cutting-edge systems and building capacities to generate, disseminate, and utilize vital data and information on climate change and its impacts on water resources and farming system.
Strengthening the extension system in the Indus Basin to ensure its ability to support the widespread adoption of locally appropriate Climate Resilient Agriculture (CRA) and On-Farm Water Management (OFWM) practices.
Supporting the adoption of CRA and OFWM practices among a critical mass of farmers, thereby increasing local awareness and demand for climate-resilient approaches to farming.
Enhancing the enabling environment to strengthen state and non-state actors to support widespread CRA and OFWM adoption and contribute to long-term agricultural transformation in the Indus Basin, post-project.
The project activities aims at effective and improved government capacity to manage water resources and information for the climate-resilient agriculture sector and society, developed farmers’ capacity to practice climate-resilient agriculture and improved rural livelihoods, providing an enabling environment where farmers can continually receive support from both the public and private sectors to sustain behavioral changes.
Resource Partner(s) | Green Climate Fund |
Budget | Total Cost (USD): 47.69 million |
Duration | Six years |
Geographic Coverage | Sindh: Umerkot, Badin and Sanghar |
Beneficiaries | 0.49 million beneficiaries living in 75 000 Households |
Implementing Partner(s) | Ministry of Climate Change (MoCC) |
Government Partner(s) | Federal Government: |
Support to SDGs
FAO Technical Assistance Services for Sindh Barrages Improvement Project (SBIP) and Sindh Water & Agriculture Transformation Project (SWAT)
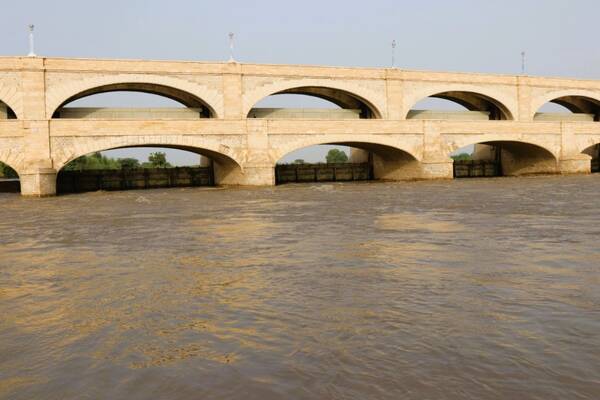

The Government of Sindh, with financial assistance from the World Bank-IDA (International Development Association), is implementing the Sindh Barrages Improvement Project. The project includes the rehabilitation and modernization of Guddu and Sukkur Barrages, as well as diagnostic studies of Kotri Barrage. The project executing agencies are the Planning and Development Department (P&DD) through its Project Coordination and Monitoring Unit (PCMU), and the Irrigation Department through its Project Management Office (PMO).
Since 2007, FAO has been involved in water and agriculture sector development interventions under the Water Sector Improvement Project (WSIP), providing project management support and technical assistance as Project Management Consultants/Procurement Agent (PMC/A). The diagnostic studies for rehabilitation of barrages were also conducted under procurement, contract management and technical assistance support of FAO as PMC/A. Building on lessons learned and success stories, the role of FAO has continued under the project charter for swift execution of this project.
FAO PMC/A has supported the planning of SWAT project, which includes FAO branded interventions such as finalization and implementation of the Sindh Water Policy, Water Accounting using latest techniques and consolidation under Aqua-Portal, Digitization of Agriculture Statistics, Farmer Field Schools (FFS) for Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA), and the establishment of value chain for agriculture products.
The expected outcomes of the Sindh Barrages Improvement Project include efficient and transparent achievement of procurement and contract management; finalization of the Sindh Water Policy, along with the completion of assessments and studies; finalization of the results framework and MEAL system for SBIP and SWAT projects; revision and finalization of the M&E Framework for the Sindh Barrages Improvement Project; and preparation of the M&E Framework for SWAT.
Resource Partner(s) | Government of Sindh through a technical assistance component of World Bank IDA loan |
Budget | USD 1.29 million |
Duration | 17 Months |
Geographic Coverage | SBIP: Kashmore, Ghotki, Sukkur, Jamshoro |
Beneficiaries | SBIP: The Project will benefit around 2.70 million people |
Implementing Partner(s) | Project Coordination and Monitoring Unit (PCMU) |
Government Partner(s) | Project Coordination and Monitoring Unit |
Support to SDGs
Enhancing Analytical Capacity of MNFSR to Manage Food Security under High Food Inflation

Sustainable growth in the agriculture sector is crucial for ensuring food security and promoting rural development in Pakistan. However, the country faces multiple challenges that have severe implications for food and nutrition security. In light of these pressing issues, it is imperative for the Ministry of National Food Security and Research (MNFS&R) to implement comprehensive and coordinated policy responses to address food security concerns effectively. The technical expertise and support of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) can play a vital role in assisting MNFS&R in addressing these challenges.
FAO experts are working closely with the officials of MNFS&R to implement the project. The technical consultants from FAO are providing their expertise and support in areas such as food price monitoring, crop analysis, and assessing the impact of floods on agriculture and food security.
The project seeks to enhance the capacity of MNFS&R in policy planning and analysis of the food security situation and food inflation in Pakistan. It is focusing on:
- Data collection, analysis, development of food price bulletins.
- Inflation and situation analyses.
- Data collection, analysis, and development of crop briefs.
- Consultation meetings with relevant stakeholders on crop situation and analysis.
- Training of relevant stakeholders in crop situation and analysis.
- Data collection, analysis, and development of a report on the impact of floods 2022 on agriculture and food security.
- Launch of the report on the impact of flood 2022 on agriculture and food security.
Resource Partner(s) | Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP) |
Budget | USD 83 000 |
Duration | 12 Months |
Geographic Coverage | Pakistan, National |
Beneficiaries | Ministry of National Food Security and Research, Other Government Ministries |
Implementing Partner(s) | N/A |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research |
Support to SDGs
Developing Capacities in Agriculture Innovation System (AIS)

The AIS project aims to address food security issues resulting from population growth by improving agricultural productivity, diversity, and nutrition outcomes while also addressing climate change and promoting resilient, effective, and sustainable agricultural practices. The project is funded by the European Union and implemented by FAO in nine countries. It supports the implementation of the Tropical Agriculture Platform (TAP) Action Plan 2018-2021 and has four outputs:
Output 1. TAP governance strengthened and TAP Secretariat operational.
Output 2. Countries’ AIS are assessed, capacity development needs are identified and AIS strengthened.
Output 3. TAP tools and approaches are integrated into Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP) ex-Pillar IV organizations, and in regional research and extension organizations in Asia-Pacific, and Latin America and the Caribbean.
Output 4. Increased awareness and knowledge on using the TAP Common Framework on Capacity Development for Agricultural Innovation Systems (CDAIS) through information and communication platforms.
In Pakistan, output 2 is being delivered over a three-year lifecycle with the following main objectives:
- To strengthen capacities for climate-relevant innovation in key organizations, and platforms or networks that provide innovation support services; and
- To strengthen the policy environment for climate-relevant agricultural innovation.
The key implementation activities include conducting a scoping study of Agriculture Innovation Systems (AIS) of Pakistan, conducting detailed assessments of innovation case studies, capacity-building activities, and measurement and evaluation of the capacity development process. The project is contributing towards promoting climate-relevant, productive, and sustainable transformation of agriculture and food systems in Pakistan.
Resource Partner(s) |
European Union |
Budget | USD 240 000 |
Duration | 2.5 years December 2020 – June 2023 |
Geographic Coverage | Punjab, Sindh and KP |
Beneficiaries | Institutes of National Agriculture Research Centre mainly: · Agriculture Engineering Institute · Climate, Energy and Water Research Institute · Crop Science Institute Agriculture Extension Departments of Punjab, KP and Sindh Ayub Agriculture Research Institute |
Implementing Partner(s)
| Ministry of National Food Security & Research (MNFSR) |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security & Research Provincial Agricultural Departments |
Support to SDGs
Balochistan Integrated Water Resources Management and Development Project (BIWRMDP)
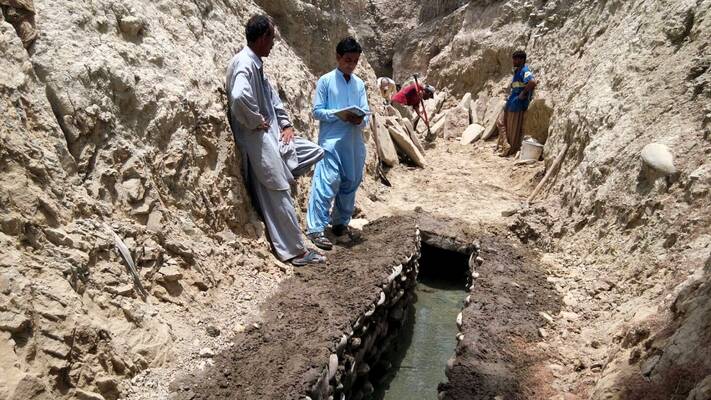

The Government of Balochistan (GoB is committed to focusing on reform and capacity building towards Integrated Water Resources Management and Development (IWRM). With the support of the World Bank, a team of experts conducted an initial review of institutional and legal reform/modernization aimed at establishing an enabling framework for IWRM. In June 2018, the GoB formally decided to initiate institutional and legal modernization involving the concerned department and designated the Irrigation Department to lead the process. Following consultations with the World Bank, the Irrigation Department invited FAO to provide technical assistance. The main objective of this project is to assist the GoB in satisfactorily implementing the BIWRMDP, with a specific focus on "Reform and Capacity Building for the Implementation of IWRM".
The Balochistan Water Policy (BWP) is being updated through regular coordination meetings with the Asian Development Bank (ADB). FAO has prepared a concept note on water modernization that incorporates a gender component. Regular technical assistance is being provided to the Project Management Unit (PMU) for general implementation of project activities. The activities include conducting a desk review and engaging in stakeholder consultations to identify threats to water resources in Balochistan and holding a provincial-level workshop for validation and consensus building.
The expected outcomes of the project are:
· Strengthening and restructuring of IWRM in Balochistan by determining appropriate institutional arrangements for the initial stages;
· Recommending a realistic trajectory for institutional change; and
· Supporting initial implementation of the roadmap for reform and/or specific action items stipulated in this roadmap.
Resource Partner(s) | World Bank |
Budget | USD 320 037 |
Duration | 2 Years |
Geographic Coverage | Balochistan |
Beneficiaries | Government of Balochistan |
Implementing Partner(s) | Irrigation Department (GoB) |
Government Partner(s) | Balochistan Government Departments · Irrigation, Forest, Agriculture, Livestock & Dairy Development · Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) · Public Health Engineering, and Water & Sanitation Authority (WASA)
|
Support to SDGs
Emergency Response to Support Livestock Owners in Flood-Affected Districts of Balochistan Province
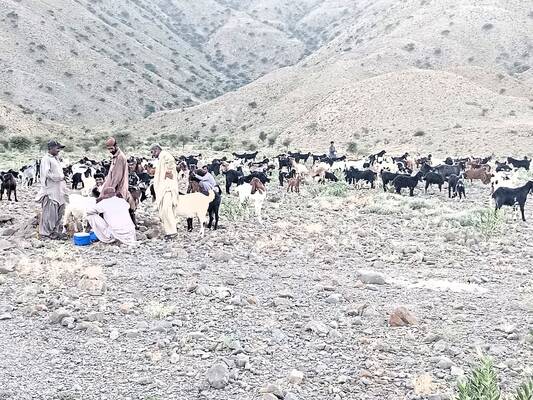

The unprecedented floods in 2022 that struck Pakistan, particularly the Balochistan and Sindh Provinces, have resulted in significant losses to livestock and agricultural lands. The agriculture sector was the hardest hit in terms of damages and second in terms of losses. Out of the estimated USD 16 billion required for recovery and reconstruction, the agriculture sector alone needs USD four billion. The floods have disrupted the supply chain for farm inputs and commodities, leading to limited access to food markets and basic nutritional necessities. Forage availability has also severely depleted. This has negatively affected livestock productivity and the production of animal-source foods that are crucial for rural households. The extensive flooding has also increased the risk of transboundary animal diseases. The situation in Balochistan was already critical before the floods, characterized by high levels of food security, malnutrition, and poverty. The floods have worsened the food security situation.
In response to the government's call for support, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) provided emergency assistance to flood-affected communities in two target districts in Balochistan: Killa Saif Ullah and Lasbella. The intervention aimed at protecting livestock assets and livelihoods through the vaccination and treatment of livestock against major diseases such as FMD, PPR, and LSD. Additionally, FAO has provide animal compound feed to mitigate the risk of starvation and improve animal welfare until the recovery phase.
Resource Partner(s) | Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP) |
Budget | USD 500 000 |
Duration | 12 Months |
Geographic Coverage | Balochistan: Lasbella and Killa Saif Ullah Districts |
Beneficiaries | Vaccination · 103 100 small animals vaccinated against PPR (the actual target was 99 000) · 7 700 large animals vaccinated against LSD & FMD (the actual target was 7 200) Animal Feed · 3 000 Households |
Implementing Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research |
Support to SDGs
Restoration of Livelihoods in Flood-Affected Districts of Dera Ismail Khan in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Rajanpur in Punjab Pakistan

Adverse monsoon weather conditions and catastrophic flooding in 2022 severely disrupted the lives and livelihoods of 33 million people in Pakistan, particularly in rural areas. Livestock experienced significant impact by the monsoon rains and flooding. Among the affected regions, Dera Ismail (DI) Khan in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) stands out as the most affected district. In Punjab, district Rajanpur experienced the highest number of livestock losses because of flash floods. The loss of livestock necessitated an immediate response supported by FAO’s Special Fund for Emergency and Rehabilitation Activities (SFERA), Belgium.
A vaccination campaign is being conducted under the project for 14,000 large ruminants and 70,000 small ruminants. 200 low-income households are being assisted for constructing model animal sheds. Training is also being provided to 40 livestock extension workers and enumerators. Additionally, fodder, feed, and molasses/urea/mineral blocks are being provided to 2,000 livestock farmers in the target districts.
FAO is implementing the project in collaboration with the Livestock and Dairy Development Departments (LDDDs) of KP and Punjab. The departments provide technical support to the project, particularly in the administration of vaccines.
Resource Partner(s) | Belgium, SFERA |
Budget | USD 500 000 |
Duration | One Year |
Geographic Coverage | Punjab: Rajanpur district Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Dera Ismail Khan district |
Beneficiaries | 7 000 livestock keepers/herders (3 500 HH each in DI Khan and Rajanpur districts) |
Implementing Partner(s)
| N/A |
Government Partner(s) | Livestock and Dairy Development Department, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
|
Support to SDGs
Support Development and Piloting Pakistan Animal Identification and Traceability System (PAITS)

Pakistan lacks an animal identification and traceability system. This project plans to develop and pilot PAITS with a suitable animal identification and traceability methodology that can enhance/support food safety and existing animal disease control efforts in Pakistan. The project is also expected to assist in improving the export of livestock products. The project is implemented directly by FAO Pakistan and overseen by a National Project Coordinator designated by the Ministry of National Food Security and Research.
Major activities under the project include holding an inception meeting and stakeholders’ workshop to establish objectives and explore options for the animal identification and traceability system in Pakistan; organizing a study visit of technical experts to countries with established animal identification and traceability systems; reviewing the legal framework pertaining to animal identification and traceability at the federal and provincial government levels; developing a comprehensive database for animal identification and traceability system; piloting implementation of PAITS in various livestock production systems; collaborating with slaughterhouses and diagnostic laboratories; and training and capacity building of different stakeholders.
Resource Partner(s) | Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP) |
Budget | USD 231 000 |
Duration | 30 Months |
Geographic Coverage | Punjab: Lahore, Bahawalpur |
Beneficiaries | 1 500 |
Implementing Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security & Research, Islamabad |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security & Research
|
Support to SDGs
Support for the Improvement of Animal Disease Surveillance System in Pakistan

The existing animal disease surveillance system in Pakistan is paper-based and fails to meet both national and international requirements. The objective of this project is to conduct a thorough evaluation of the current animal disease reporting system at multiple levels and propose a comprehensive animal disease surveillance system tailored to national needs. The project is implemented directly by FAO Pakistan and overseen by a National Project Coordinator designated by the Ministry of National Food Security and Research.
The project seeks to achieve its objective by reviewing the progress made in enhancing animal disease surveillance in Pakistan, evaluating the capacity and effectiveness of the current animal surveillance system using the Surveillance Evaluation Tool (SET) framework, conducting on-site inspections to verify the Animal Disease Surveillance Setup in each province/administrative unit, developing a new animal disease surveillance mechanism specifically designed for Pakistan, and outlining the necessary IT infrastructure for the proposed real-time Animal Disease Surveillance (ADS) system.
Resource Partner(s) | Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP) |
Budget | USD 178 724 |
Duration | 18 MonthsOctober 2022 – March 2024 |
Geographic Coverage | Punjab, Sindh, Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Azad Jammu & Kashmir, Gilgit-Baltistan, and Islamabad Capital Territory |
Beneficiaries | Federal Government and all Provincial Livestock Departments |
Implementing Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security & Research, Islamabad |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security & Research |
Support to SDGs
Transforming the Indus Basin with Climate Resilient Agriculture and Water Management
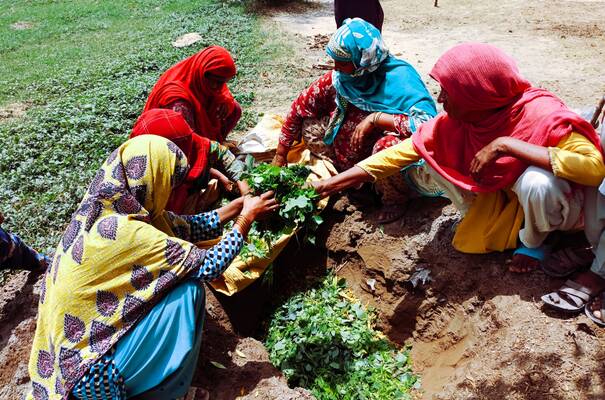

Climate change poses significant threats to the future livelihoods of farmers and the agriculture sector around the Indus Basin in Pakistan. The project was designed to address climate challenges by departing from the “business as usual” approach and through smart water management in the Indus Basin. It aims to increase resilience to climate change among the most vulnerable farming community in the Indus Basin and to strengthen public/private sector capacity for the development of climate-smart agriculture.
The project will achieve its objectives through:
· Establishing cutting-edge systems and building capacities to generate, disseminate, and utilize vital data and information on climate change and its impacts on water resources and farming system;
· Strengthening the extension system in the Indus Basin to ensure its ability to support the widespread adoption of locally appropriate Climate Resilient Agriculture (CRA) and On-Farm Water Management (OFWM) practices;
· Supporting the adoption of CRA and OFWM practices among a critical mass of farmers, thereby increasing local awareness and demand for climate-resilient approaches to farming; and
· Enhancing the enabling environment to strengthen state and non-state actors to support widespread CRA and OFWM adoption and contribute to long-term agricultural transformation in the Indus Basin, post-project.
Initiatives under the project include developing a water accounting system; establishing an evapotranspiration (ET) based water management system; improving availability and use of information services; improving farming practices for climate resilience; training of trainers on CRA and OFWM; developing farmers’ capacity to transform agriculture practices with CRA and OFWM.
Resource Partner(s) | Green Climate Fund Government of Punjab Government of Sindh |
Budget | Total Cost (USD): 47.69 million Green Climate Fund (USD): 34.99 Million Government of Punjab (USD): 7.99 million Government of Sindh (USD): 4.69 million |
Duration | Six years March 2020 – March 2026 |
Geographic Coverage | Punjab: Dera Ghazi Khan, Muzaffargarh, Khanewal, Multan, and Lodhran Sindh: Umerkot, Badin and Sanghar |
Beneficiaries | 1.3 million beneficiaries living in 200 000 Households |
Implementing Partner(s) | Ministry of Climate Change (MoCC) Provincial Agriculture and Irrigation Departments |
Government Partner(s) | Federal Government: Ministry of Climate Change (MoCC) and Line Departments Provincial Government: Agriculture and Irrigation Departments, Government of Punjab Agriculture and Irrigation Departments, Government of Sindh Support to SDGs |
Data Collection Survey on Improvement of Livelihoods and Food Security through Agriculture for the Afghan Refugees and Host Communities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa

FAO and JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency) agreed to assess the refugee camps in Kohat and Haripur districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) to examine the food security, livelihoods, socioeconomic conditions, and resilience of the Afghan refugees. Additionally, the project is evaluating the impact of their presence on the host communities. The findings will assist FAO and its development partners in formulating future programme activities aimed at supporting both the refugees and host communities in KP.
The project has been designed in consultation with UNHCR (United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees), CAR (Commissionerate for Afghan Refugees), and Green Sector line departments. It is devised to be in line with various policy frameworks and guidelines, including the 1951 Refugees Convention and its 1967 Protocol, the National Policy on Afghan Refugees 2013, Pakistan's Strategic Trade Policy Framework 2020-2025, KP-Agriculture Policy 2015, and KP-Livestock Policy 2018.
Key activities under the project include provision of certified wheat seeds and fertilizer; development of fruit plants nurseries, orchards, and seasonal vegetable production enterprises, off-season vegetable production through tunnel farming; rehabilitation of irrigation channels through cash-for-work programme; training on water-saving and collection to improve water use efficiency; vaccination and deworming of animals; provision of dairy goats; backyard poultry packages; and small-scale incubators to women.
Resource Partner(s) | JICA Pakistan |
Budget | USD 846 966 |
Duration | 18 Months 31 March 2023 – 30 September 2024 |
Geographic Coverage | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Kohat and Haripur Districts |
Beneficiaries | 2 692 Households (HHs) |
Implementing Partner(s)
| Community-Based Organizations (CBOs) Farmers’ Associations Private Sector Multilateral donors |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research Ministry of Commerce United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) Commissionerate of the Afghan Refugees in KP Planning and Development Department, Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Agriculture Department, Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Academia and Research Institutions |
Support to SDGs
Emergency Livelihood Assistance to Flood-Affected Communities in Balochistan and Sindh Provinces

Pakistan’s agriculture sector has experienced significant losses and extensive damage as a result of the heavy floods in 2022, necessitating immediate assistance. The "2022 Floods Response Plan" estimates that approximately 14.6 million people are in need of food security and agricultural assistance. It is imperative to provide immediate nutritional support to highly food-insecure people, while simultaneously supporting the restoration of crop and livestock-based livelihoods and rehabilitating productive assets. Without such assistance, the decline in crop and livestock production and productivity will persist, further undermining food security, nutrition trends and leading to long-term dependence on food aid.
The project is implemented through implementing partners, for which FAO builds the capacity. These partners carry out beneficiary assessments and distribute agriculture and livestock inputs to affected individuals in the target districts of Sindh and Balochistan. FAO guides, trains, supervises these partners, and manages all procurement of inputs and expendable items, including the procurement process, technical specifications, and quality assurance measures.
The project provides life-saving livelihood support to agriculture-dependent households affected by floods to address food and nutrition insecurity. It also helps in safeguarding the livestock assets of agro-pastoral and pastoral households affected by the flood.
Resource Partner(s) | Government of Japan (JPN) |
Budget | USD 6 481 481 |
Duration | 12 Months March 2023 – March 2024 |
Geographic Coverage | Sindh: Districts Sanghar and Badin Balochistan: Districts Pashin and Jhal Maghsi |
Beneficiaries | 38 400 HHs |
Implementing Partner(s) | Hands NGO, District Badin, Sindh Province Sindh Agricultural Forestry Workers & Coordinating Organization (SAFWCO) for District Sanghar, Sindh Province Water, Environment and Sanitation Society (WESS) for Districts Pishin and Jhal Magsi, Balochistan Province |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of Food Security and Research (MNFSR) National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) Provincial Disaster Management Authority (PDMA) Livestock and Dairy Development Department (LDDD) Agriculture and Livestock Development Directorates, Sindh and Balochistan Federal Seed Certification and Registration Department (FSCRD) District Administration Irrigation Department |
Support to SDGs
Emergency Response to Support Livestock Owners in Flood-Affected Districts of Sindh Province

Severe monsoon rains triggered devastating floods and landslides across Pakistan, with Balochistan and Sindh provinces bearing the brunt of the disaster. The 2022 floods caused loss of life and displacement, inflicted substantial damage on agricultural lands, livestock, forests, and vital civil and agricultural infrastructure. The floods and landslides also caused extensive destruction to agriculture-related infrastructure, including animal shelters, fishponds, on-farm irrigation systems, and equipment. The World Bank estimates that the national poverty rate could potentially increase by 4.5 to 7.0 percentage points, pushing between 9.9 and 15.4 million people into poverty and exacerbating the hardships faced by already impoverished households.
FAO Pakistan in close collaboration with Livestock Development Department, Sindh, United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs and with the support of Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF) launched mass vaccination campaigns in four districts of Sindh, namely Dadu and Khairpur, Larkana, and Naushahro Feroz, as part of the CERF Project Sindh. After receiving endorsements from the most vulnerable union councils in four districts, the district administration collaborated with the provincial and district livestock departments to devise an implementation strategy for a vaccination campaign and providing supplementary feed to animals in order to restore their essential source of nutritious food, saving the lives of the flood-affected households. The campaign benefitted 3 000 households in each district.
Resource Partner(s) | United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA) |
Budget | USD 1 404 280 |
Duration | Nine Months |
Geographic Coverage | Sindh: Dadu, Khairpur, Naushero Feroz, and Larkana Districts |
Beneficiaries | 30 000 Households (HHs) Distribution of animal feed to 12 000 HHs (36 000 bags of 50 kg each) |
Implementing Partner(s)
| Sindh Livestock Department (SLD) |
Government Partner(s) | Livestock Department, Government of Sindh |
Support to SDGs
Strengthening Resilience of Agro-Pastoralists in Sindh (SRAS)
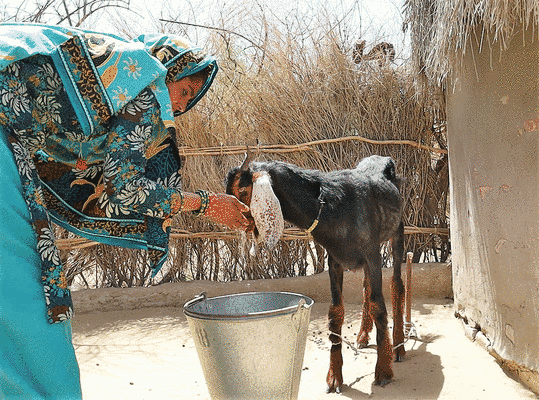
The “Strengthening Resilience of Agro-Pastoralists in Sindh” (SRAS) project is set to play a crucial role in the European Union’s comprehensive support for the Sindh province. The project focuses on addressing poverty, food insecurity and malnutrition, while also aiming to enhance the resilience of targeted communities in the face of climatic and economic shocks. The project is implemented in two districts of Sindh province, Umerkot and Tharparkar. With a target of reaching 37 900 vulnerable farming households, the SRAS project is expected to have a positive impact on their food security, resilience, and livelihoods.
The project is implemented directly by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) through its provincial and field-based offices in the Sindh province. The key government counterparts for the project are Livestock Department, Forest Department, Agriculture Extension Department, Provincial Disaster Risk Management Authority (PDMA) and Arid Zone Research Institute.
The project is expected to have the following outcomes:
· Sustainable agricultural and livestock production by food insecure smallholder farming households in Tharparkar and Umerkot during the COVID-19 crisis and strengthening it later.
· Food supply to local and provincial food markets is ensured, particularly by smallholder farmers in the two districts.
Resource Partner(s) | European Union |
Budget | USD 3 668 126 |
Duration | Four years |
Geographic Coverage | Sindh: Umerkot and Tharparkar Districts |
Beneficiaries | 37 900 Farming Households |
Implementing Partner(s) | FAO through its Provincial and Field-based Offices in Sindh Province |
Government Partner(s) | Livestock Department |
Support to SDGs
Livelihood and Food Security Improvement Activity for Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Merged Districts and the Flood Affected Areas of Pakistan

FAO Pakistan has been implementing the USAID-funded Livelihood and Food Security Improvement Activity (LFSA) for improving livelihoods, food security and resilience of the targeted rural communities through the agriculture-led growth in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, provision of nutrition support in Sindh and assisting population affected by the 2022 monsoon floods in the country. The goal of the project is to achieve restoring impaired cropping systems and inspiring adoption of technological advancements for enhanced productivity and better livelihoods through reinforcing and supporting agriculture and livestock sectors with assets creation and diversification of livelihoods opportunities for better nutrition and increased resilience of the vulnerable population, youth and women.
The LFSA has three distinct components relating to the emergency flood response (across the country), agricultural development work in the newly Merged Districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP-NMDs) and relief and rehabilitation specific actions focusing on nutrition in the Shaheed Benazir Abad District of Sindh Province. The first quarter (October-December 2022) of the Year-1 (Oct. 2022-Sept. 2023) of the project, was focused on component one undertaking delivery of Rabi Packages of certified wheat seed and required fertilizers. The second component is focused on undertaking series of agriculture sector development activities in KP province for the duration of the project. The third component is designed for the duration of two years and focuses on provision of nutrition support to the flood affected communities in Sindh province.
Resource Partner(s) | USAID Pakistan |
Budget | Total: USD 25,000,000 Component 1 – USD 8,500,000 Component 2 – USD 12,500,000 Component 3 – USD 4,000,000 |
Duration | Four years October 2022 – September 2026 |
Geographic Coverage | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Newly Merged & Flood Affected Districts Sindh: Shaheed Benazir Abad & Flood Affected Districts Punjab: Flood Affected Districts |
Beneficiaries | KP NMDs: 104,008 households Flood affected areas: 66,403 households Sindh: 100,000 households Total: 270,411 households |
Implementing Partner(s)
| Community-Based Organizations (CBOs) Farmer Field Schools (FFS), Producer Marketing Groups (PMG) and Farmers’ Marketing Collectives (FMCs),Private Sector Multilateral Donors. UN- Women and World Food Programme (WFP) |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research Provincial Agricultural Line Departments |
Support to SDGs
Control of Transboundary Livestock Diseases (Foot and Mouth Disease & Peste des Petits Ruminants)

Several years back, the Livestock & Dairy Development Department of Punjab requested the assistance of FAO Pakistan to develop and implement control programmes for Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) and Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) in selected areas of the province. These two Transboundary Animal Diseases (TADs) result in annual economic losses exceeding USD one billion. The objective of the project is to minimize their economic impact. FAO implements this project through the veterinary field staff of the province. The National Veterinary Laboratory of Islamabad provides training in FMD and PPR diagnosis.
The project activities include training veterinary field staff, raising awareness among livestock farmers, strengthening diagnostic laboratories for FMD and PPR, establishing a rapid response mechanism for controlling outbreaks, enhancing cold chain facilities for vaccines, conducting preventive vaccination against PPR and FMD in selected areas, and performing clinical and sero-monitoring for FMD and PPR of animals in the vaccinated area.
The expected outcomes include reduction in the prevalence of the two most common TADs in the project area, thus improving the profitability of livestock in the region.
Resource Partner(s) | Government of Punjab (Livestock & Dairy Development Department) |
Budget | USD 39 948 386 |
Duration | 84 MonthsJanuary 2017 – December 2023 |
Geographic Coverage | Punjab (Preventive vaccination in Bahawalpur, Bahawalnagar, Rahim Yar Khan and Cholistan districts of South Punjab and in Sahiwal, Pakpattan, Okara, Sheikhupura, Vehari, other activities in emergency vaccination all districts of Punjab) |
Beneficiaries | 1 668 958 (FMD: 995 936, PPR: 673.022) |
Implementing Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security & Research Livestock & Dairy Development Department, Government of Punjab |
Government Partner(s) | Livestock & Dairy Development Department, Government of Punjab |
Support to SDGs
Growth for Rural Advancement and Sustainable Progress (GRASP)

The GRASP programme aims to alleviate poverty and promote sustainable, inclusive economic growth in the Sindh and Balochistan provinces. These regions rely heavily on agriculture, but face challenges such as low productivity, high post-harvest losses, and limited agro-processing capabilities. The programme seeks to address these issues by strengthening small-scale agribusinesses in the horticulture and livestock sectors.
FAO will implement the programme by supporting and building the capacity of male and female farmer groups in both the provinces. This will include efforts to enhance productivity, improve product quality, and adapt to the impacts of climate change. The programme will also focus on value addition through improved packaging, grading, storage, and processing, as well as connecting farmer groups with markets.
Key activities of the programme include providing agricultural extension services to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), building climate change awareness among farmer associations, training primary producers and SMEs on value addition techniques, and establishing Farmer Marketing Collectives (FMCs). The programme also aims to empower rural women by providing support for economic opportunities related to agricultural production and value addition.
The expected outputs of the programme include the promotion of Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) practices and technologies, strengthening the capacities of micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) to add value to agricultural products, empowering rural women, and enhancing the business management and marketing capacities of farmer organizations.
Resource Partner(s) | European Union through International Trade Centre (ITC) |
Budget | USD 9 729 845 |
Duration | 54 Months September 2019 to March 2024 |
Geographic Coverage | Sindh Province: Thatta, Karachi, Hyderabad, Matiari, Tando Muhammad Khan, Mirpurkhas, Tando Allahyar, Sanghar, Shaheed Benazirabad, Khairpur, and Tharparkar Balochistan Province: Kharan, Nushki, Kech, Panjgur, Zhob, Musakhail, Quetta, Pishin, Las Bela, and Khuzdar |
Beneficiaries | 33 000 Households |
Implementing Partner(s) | FAO is implementing the project directly in collaboration with government partners |
Government Partner(s) | Federal Level: · Ministry of Economic Affairs · Ministry of Commerce Provincial-level – Balochistan: · Department of Agriculture and Cooperatives (DoAC) · Livestock and Dairy Development Department (LDDD) · Food Department · Planning and Development Department, Government of Balochistan Provincial-level – Sindh: · Agriculture, Supply & Prices Department · Livestock & Fisheries Department · Food Department · Planning and Development Department, Government of Sindh |
|
|
Support to SDGs
Emergency Livelihood Assistance to Flood-Affected Communities in Balochistan and Sindh Provinces

Pakistan’s agriculture sector has experienced significant losses and extensive damage as a result of the heavy floods in 2022, necessitating immediate assistance. The "2022 Floods Response Plan" estimates that approximately 14.6 million people are in need of food security and agricultural assistance. It is imperative to provide immediate nutritional support to highly food-insecure people, while simultaneously supporting the restoration of crop and livestock-based livelihoods and rehabilitating productive assets. Without such assistance, the decline in crop and livestock production and productivity will persist, further undermining food security, nutrition trends and leading to long-term dependence on food aid.
The project is implemented through implementing partners, for which FAO builds the capacity. These partners carry out beneficiary assessments and distribute agriculture and livestock inputs to affected individuals in the target districts of Sindh and Balochistan. FAO guides, trains, supervises these partners, and manages all procurement of inputs and expendable items, including the procurement process, technical specifications, and quality assurance measures.
The project provides life-saving livelihood support to agriculture-dependent households affected by floods to address food and nutrition insecurity. It also helps in safeguarding the livestock assets of agro-pastoral and pastoral households affected by the flood.
Resource Partner(s) | Government of Japan (JPN)
|
Budget | USD 6 481 481
|
Duration | 12 Months March 2023 – March 2024
|
Geographic Coverage | Sindh: Districts Sanghar and Badin Balochistan: Districts Pashin and Jhal Maghsi
|
Beneficiaries | 38 400 HHs
|
Implementing Partner(s) | Hands NGO, District Badin, Sindh Province Sindh Agricultural Forestry Workers & Coordinating Organization (SAFWCO) for District Sanghar, Sindh Province Water, Environment and Sanitation Society (WESS) for Districts Pishin and Jhal Magsi, Balochistan Province
|
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of Food Security and Research (MNFSR) National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) Provincial Disaster Management Authority (PDMA) Livestock and Dairy Development Department (LDDD) Agriculture and Livestock Development Directorates, Sindh and Balochistan Federal Seed Certification and Registration Department (FSCRD) District Administration Irrigation Department
|
Support to SDGs
Alternative Livelihood through High Value Crops in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (ALOP)

The project focuses on selected newly merged tribal districts where illicit crops are cultivated, causing detrimental socio-economic impacts on local communities and beyond. The project aims to expand the adoption of successful practices for developing alternative livelihoods, while encompassing the entire value chains of high-value crops through participatory approaches. It seeks to enhance the profitability of value chains by building the capacities of actors within the value chains, as well as related service providers and other relevant stakeholders.
The project is implemented by FAO in collaboration with line departments. The project capitalizes on the existing Agriculture Extension Department’s network and strengthen it to increase farmers’ access to extension services.
The project introduces high value crops, enhances livestock breed, improves irrigation channels, organizes and strengthens Farmer Field Schools (FFS), establishes Farmer Business schools (FBS) implements technology-based value addition aligned with buyers’ requirements, establishes market linkages, and builds the capacity of the Agriculture Department in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
Resource Partner(s) | International Bureau of Narcotics Control and Law Enforcement (INL), State Department, Government of the United States of America (USA)
|
Budget | USD 1 300 627 |
Duration | Four Years and Nine Months September 2018 – June 2023 |
Geographic Coverage | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Bajaur, Mohmand, Khyber, Orakzai, and Torghar Districts |
Beneficiaries | 1 510 Producers (970 Men and 540 Women) 73 Market Intermediaries 20 Women Processors 50 Government Staff and Facilitators |
Implementing Partner(s)
| FAO is directly implementing the project |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research Department of Agriculture, Civil Secretariat, Peshawar Agriculture Extension Department, Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
Support to SDGs
Technical Support for Formulation of Tea Commercialization and Cluster-based Development Plan in Pakistan

After petroleum products and edible oil, tea is the third major import commodity in Pakistan. Pakistan has been struggling to boost domestic tea production for the last 20-30 years. Tea development projects have yielded underwhelming returns and failed to convince farmers to engage in the large-scale cultivation. The tea sector has remained undersized mainly due to lack of long-term programmatic approach and public-private coordination, weak institutional support, and ineffective production methods.
This project aims to provide a comprehensive plan for tea commercialization and cluster-based development, laying the groundwork for future projects. The execution is being carried out by FAO in close collaboration with Ministry of National Food Security and Research, Pakistan Agricultural Research Council through NTHRI, and the Agriculture, Forest, and Tourism departments of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP). Relevant district administration and stakeholders will be involved in consultation for site surveys, cluster formation, and other tasks.
The expected results include preparing a comprehensive plan for tea commercialization through public-private partnerships and the establishment of tea estates, developing a plan for cluster-based tea development through identification of suitable areas and engagement of farmers for tea plantation, establishing the Tea Development Board in Pakistan and formulating a plan for tea-based ecotourism under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
Resource Partner(s) | Technical Cooperation Programme (TCP)
|
Budget | USD 225 000
|
Duration | One Year January 2023 – December 2023 |
Geographic Coverage | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Mansehra, Battagram, and Swat Districts
|
Beneficiaries | Targeted number of public and private sector entities, and local farmers of Mansehra, Battagram, and Swat districts |
Implementing Partner(s)
| FAO |
Government Partner(s) | Ministry of National Food Security and Research National Tea and High Value Crops Research Institute (NTHRI) Pakistan Agriculture Research Council (PARC) Provincial Agriculture Department of KP Forest and Tourism Departments of KP Academia and Research Institutions |
The Revival of Balochistan Water Resources Programme (RBWRP)

Balochistan faces multiple challenges in managing its natural resources, especially water and rangelands, which are vital for its agricultural and livestock sectors. The province needs to adopt efficient water use and sustainable rangeland management practices to achieve its economic potential and reduce poverty and inequalities.
The RBWRP is a 4.5 year programme that aims to improve income and food security in selected river basins through sustainable agricultural and livestock farming systems based on sustainable, equitable management of water and rangeland resources. The programme is introducing environmentally sustainable resource management practices to cope with the effects of climate change. The RBWRP is expected to have four outcomes:
- Effective governance structures that will sustainably and equitably deliver evidence-based oversight of water and rangeland resources at provincial, river basin, watershed, and community levels.
- Transition to low water use agriculture and livestock farming systems.
- Water efficient and profitable agricultural value chains.
- Enhanced core capacities of government institutions, academia, community, and the private sector to support and manage their water and rangeland resources sustainably and equitably.
Duration: | April 2022 – September 2026 (4.5 years) |
Resource Partner: | European Union (EU) |
Budget: Total Budget | = 40 million EUR |
Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN | = 27 million EUR |
Technical Assistance Partner | = 13 million EUR |
Implementing Partners: | Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations Landell Mills International (LMI) in consortium with the International Water Management Institute (IWMI) |
Beneficiaries: | 59,430 Households - 416,000 Individuals |
Alignment to SDGs
Japan Fund for Prosperous and Resilient Asia and Pacific (JFPR) Grant Balochistan Urgent Response for Food Security Project, Pakistan

The Balochistan Urgent Response for Food Security Project aims to revive agricultural production in four severely flood affected districts of Nasirabad Division: Nasirabad, Jaffarabad, Usta Mohammad and Sohbatpur. The purpose of this project is to protect the flood-affected population from poverty and food insecurity by restoring their socio-economic conditions to pre-flood levels using the Build Back Better Framework approach.
The target groups under this project are rural farm households, including women whose cultivated lands were the most severely damaged by floods. The project incorporate measures to strengthen community resilience to disasters caused by natural hazards. It will contribute to improved food security and livelihood of 30% of farm households in the target districts through the following interventions:
- Provision of climate adaptive certified rice seed, safer and more durable small tools and protective footwear to 60,000 farm households in the target districts.
- Protective footwear will also be provided to 7,500 women laborers from targeted farm households to enable safe rice transplanting activities. In addition, they will receive safer and more durable small tools to facilitate their work in women-led farming.
The collaboration between Balochistan Agriculture & Cooperatives Department (BACD) and FAO is the first time FAO has received funds by and through a government as a recipient of funding from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) that is financed by the Japan Fund for Prosperous and Resilient Asia and the Pacific (JFPR).
Duration: | March – September 2023 |
Resource Partner: | Japan Fund for Prosperous and Resilient Asia Pacific (JFPR) Grant |
Budget: | US$ 5 million |
Executing Agency: | Balochistan Agriculture and Cooperatives Department (BA&CD) |
Implementing Partners: | Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations |
Beneficiaries: | 60,000 Farm Households |
Alignment to SDGs
Feasibility Study and Piloting of Farming of new Shrimp/ Prawn and Fish species in Punjab and Sindh Provinces

Fisheries resources offer opportunities for sustainable development and exploitation of various varieties of edible fish in the process generating both employment opportunities and economic benefits, largely for rural communities. The country's fisheries sector is comparatively small. It contributes only 0.8 percent to overall Gross Domestic Product (GDP), 3.7 percent to Agriculture GDP and less than 1 percent to national employment. Aquaculture is an important fisheries sub-sector that has substantial potential to significantly contribute to food security, poverty reduction, employment creation and reduction of pressure on capture fisheries resources. The Government of Pakistan has recognized the importance of the fisheries and aquaculture sector and is supporting the sector for import substitution and production of exportable surplus. Recently, the Government has launched a comprehensive 309 billion rupee “Agriculture Emergency Programme”, under which three of its thirteen development projects would be executed in fisheries which include projects on incubating shrimp farming, cage culture for fish species and trout culture in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
In an effort to support the government, this project seeks to conduct a feasibility study identifying new shrimp/prawn and fish culture species in Punjab and Sindh provinces with good aquaculture practices. Site selection and zonation mapping would be covered under the feasibility which is critical for promoting aquaculture in Pakistan.Duration: August 2019 to December 2020
Resource Partner(s): Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations (FAO), Pakistan
Budget: USD 195,000
Implementing Partner(s): Ministry of National Food Security & Research through the Fisheries Development Board (FDB), Islamabad
Alignment to SDGs


Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives
Two model demonstration units will be setup for new shrimp and fish species with best management aquaculture practice and financial feasibility to motivate the private sector for investment in this sector.
Restoration of Livelihoods in FATA (Phase II)

This three-year initiative, with the financial assistance of the Government of Japan through the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), is helping returnee families resume agricultural production and restart normal economic activities, reduce poverty and economic inequalities through sustainable agriculture development in the two selected tribal districts – Kurram and Khyber of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
The project focuses on improving agricultural productivity through innovative farming practices, technologies and value addition in agriculture through the establishment of value chain and functional markets. The project also aims to achieve adoption of climate smart and resilient agriculture; dissemination and adoption of practices for increasing livestock, poultry and inland fisheries production. With the decade long abandonment of land, the project is introducing water harvesting methods and rehabilitation of irrigation structures. An innovative approach of development and implementation of Integrated Natural Resource Management (INRM) in both districts is being adopted. The project is developing agricultural and livestock value chains by establishing a linkage between farmers and market.
Duration: April 2018 – March 2021
Resource Partner(s): Japan International Cooperation Agency-JICA
Budget: USD 4.9m
Implementing Partner(s): FAO
Beneficiaries (approximate number):32 651 Households
Alignment to SDGs




Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
- Help eliminate hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition
- Make agriculture, forestry and fisheries more productive and sustainable
- Reduce rural poverty
- Enable inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems
Restoration of Livelihoods in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Tribal Districts

The tribal districts in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province have a predominantly agrarian economy, based primarily on arable agriculture, livestock, fisheries and forestry. FAO, with partner agencies, has provided agriculture/livestock related support to the Temporarily Displaced Persons (TDPs) who have returned to their homes, engaging them in market oriented and commercial agriculture to help stabilize the area.
The project is assisting about 42 000 households in four selected tribal districts designated as high priority areas for Food Security, and Health and Protection – the target districts include Kurram, Orakzai, North Waziristan and South Waziristan of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The project focuses on providing holistic support to the families returning to the area. This approach covers a significant range of sustainable development activities including introduction of climate smart resilient practices and technologies in return areas; value chain development, water management, Integrated Natural Resource Management and capacity development. Through this project, the agricultural productivity of the region will be improved through climate resilient practices and developing value chains by linking farmers with the local and national markets.
Duration: November 2018 - April 2020
Resource Partner(s): DFID
Budget: USD 13.38m
Implementing Partner(s): FAO, UNICEF, UNWOMEN
Beneficiaries (approximate number): 42,000 HHs
Alignment to SDGs





Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
- Help eliminate hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition
- Make agriculture, forestry and fisheries more productive and sustainable
- Reduce rural poverty
- Enable inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems
Technical support for designing Agriculture and Natural Resource Management (ANR) related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) programmes/plans

The project will contribute to the eradication of hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition in Pakistan.
A brief analysis of the 17 global SDGs and their targets reveals that seven SDGs are entirely related to the generic thematic areas of agriculture and natural resources management (ANR). To address this vital subject, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations in Pakistan initiated the support to the Government of Pakistan in designing a road map for ANR SDGs process.
Duration: 1 year (May 2019- April 2020)
Resource Partner(s): TCP, FAO
Budget: USD 50,000
Implementing Partner: Ministry of National Food Security & Research, Government of Pakistan
Alignment to SDGs

Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
The TCP project is fully aligned with the Sustainable Development Framework for Pakistan, the Vision 2025, 12th Five Year Plan 2018-23 and the FAO’s Country Programming Framework and following Strategic Objectives (SOs).
SO1- Help eliminate hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition
SO2 - Make agriculture, forestry and fisheries more productive and sustainable;
SO3 - Reduce rural poverty;
SO4 - Enable inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems
Restoring Subsistence and Commercial Agriculture in FATA

The tribal districts in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, previously known as FATA, are one of the most underdeveloped regions of Pakistan. The vast majority of the population resides in rural areas, and livelihoods are based on subsistence level agriculture and livestock. Due to the security insurgencies, thousands of people became Temporarily Displaced Persons (TDPs) for decades who have now returned to their region. FAO is assisting in revitalizing the livelihoods of the returning TDPs through various interventions. The project aims to significantly contribute to the stabilization of the region by reducing poverty and economic inequalities through:
- Resumption of food production and restoration and improvement of agriculture-based livelihoods in target areas;
- Restoration or establishment of market structures and services; and,
- Capacity development of the communities and partners, an integral component of the project.
The project addresses both the short-term recovery and rehabilitation needs of those who have remained in the area as well as those returning or who have recently returned, and focusing on the long-term agricultural development needs of the target communities. The project will result in: increased availability of land, water, seeds, and other quality inputs; improved quality and exchange of agricultural knowledge; and, the introduction of technologies leading to greater agricultural production.
Duration: July 2017 – June 2020
Resource Partner(s): USAID
Budget: USD 10 Million
Implementing Partner(s): FAO
Beneficiaries (approximate number): 42,763 HH (316,446 individuals)
Alignment to SDGs





Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
- Help eliminate hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition.
- Make agriculture, forestry and fisheries more productive and sustainable.
- Reduce rural poverty.
- Enable inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems.
Support in Implementing the Agriculture and Livestock Policies in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa

Support in Implementing the Agriculture and Livestock Policies in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa project focuses on strengthening planning capacities in the Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) to develop needs-based Action Plans and Implementation Strategies for Agriculture and Livestock policies.
The project is supporting key staff in the Departments of KP Livestock and Dairy Development and Agriculture Extension to strengthen their policy planning skills. These enhanced capacities will support the process to develop and revise comprehensive and effective Action Plans leading to successful policy implementation. These policies aim to benefit the farming communities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by improving food security and nutrition and increasing their income.
Project Profile
Resource Partner: FAO
Budget: USD 50,000
Duration: May/June 2019 – 2020
Beneficiaries: KP Agriculture Department and Livestock Department, KP farming community
Implementing Partners: KP Agriculture and Livestock Departments
Geographic Coverage: Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province
Government Counterparts: KP Agriculture, Livestock, Fisheries and Cooperative Department
Relevant SDGs


Support to develop a National Policy and Implementation Plan for Fisheries & Aquaculture sector

Pakistan is endowed with fishery and aquatic resources that have significant potential to make a bigger contribution to economic growth and social development. At present, fisheries contribute modestly to the national and local economy. The underlying potential of Pakistan’s fisheries and aquatic resources is not reflected in current production, growth, and value. The sector has much more to offer in terms of boosting export revenues, creating decent jobs, supporting livelihoods in coastal communities, improving domestic nutrition and food security, and closing Pakistan’s significant economic gender inequality. The Government of Pakistan recognizes these opportunities and has signaled its desire to increase the contribution of the fishery sector towards these goals. The development of fisheries sector is a key priority within the country’s Poverty Reduction Strategy as well. Recently, the Government has launched a comprehensive 309 billion rupee “Agriculture Emergency Program”, under which three of its thirteen development projects would be executed in fisheries which include projects on incubating shrimp farming, cage culture for fish species and trout culture in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
In order to strengthen the implementation of these development projects, there is an urgent need to conduct a holistic sectoral analysis of the fisheries and aquaculture sector in Pakistan to identify the missing gaps and constraints hindering the sector and opportunities for its development. Building on this premise, the Government of Pakistan intends to conduct a sectoral analysis of the fisheries and aquaculture sector of the country and to frame a National Fisheries and Aquaculture Policy, Strategy and Action Plan with the assistance of FAO, to create an enabling environment for speedy development and promotion of fisheries sector on a sustained basis.
Duration: August 2019 to July 2020
Resource Partner: Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations (FAO), Pakistan
Budget: USD 68,000
Implementing Partner: Fisheries Development Board, Ministry of National Food Security & Research, Islamabad
Alignment to SDGs

Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
- To prepare draft National Fisheries and Aquaculture Policy, Strategy and Action Plan
- To review the existing federal and provincial fisheries legislations and propose revision/ updating to incorporate the international fisheries instrument’s obligations.
FAO’s Technical Assistance to the UK/DFID-funded “Building Disaster Resilience in Pakistan” Programme

The United Kingdom Department for International Development (UK/DFID) – funded “Building Disaster Resilience in Pakistan (BDRP)” Programme aims to increase Pakistan’s capability to reduce disaster risk though better planning, preparedness and response at the government and community levels. BDRP works through two main delivery areas: (a) Community Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM); and (b) Strengthening disaster management bodies at the federal, provincial, district and community levels in line with the Government of Pakistan’s National Disaster Management Plan (2012-2022) while contributing towards the achievement of the overall goal and outcome of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.
(a) Community Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM); and (b) Strengthening disaster management bodies at the federal, provincial, district and community levels in line with the Government of Pakistan’s National Disaster Management Plan (2012-2022) while contributing towards the achievement of the overall goal and outcome of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.
Duration: September 2018- August 2020
Resource Partner(s): UK-DFID
Budget: USD 3,901,170 (GBP 3,000,000)
Implementing Partner(s): FAO, UNDP and WFP
Beneficiaries (approximate number): 5, 400 beneficiaries
Alignment to SDGs

Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
SO2 - Make Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries more Productive and Sustainable
SO5 - Increase the resilience of livelihoods to threats and crises
Multi-Year Humanitarian Program (MYHP)

In view of the constraints faced by vulnerable communities in the aftermath of localized and large-scale disasters, the Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations (FAO), together with development partners, launched a five-year program under the umbrella of the Natural Disasters Consortium (NDC), set up under Pillar 1 of the Department for International Development (DFID)-funded Multi-Year Humanitarian Program (MYHP) in Pakistan.
Since the establishment of the consortium, FAO continues to deliver a wide range of food security focused inclusive, coherent and good-value preparedness, response and recovery support to vulnerable communities across Pakistan. Local capacities built, life-saving needs have been provided and community-based recovery structures are strengthened. FAO’s objective is to contribute to enhancing resilience-building measures across the disaster affected/disaster prone areas.
Additionally, while adhering to its strict mandate, the FAO (under NDC) established initiatives which feature innovative, resilient and inclusive solutions for underprivileged farmers; thereby, supporting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Pakistan.
Duration: Five years (2015 - 2020)
Resource Partner(s): Department for International Development (DFID)
Budget: USD 6,703,725
Implementing Partner(s):
- Agha Khan Rural Support Program
- Relevant Government Line Departments
Alignment to SDGs:





Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
MYHP has been designed and implemented in alignment with strategic objective 5 (SO-5) of globally agreed FAO’ objectives. Therefore, project contributed to the increased resilience and preparedness by reducing the risks to the food and agricultural systems of local communities.
The Australia Balochistan Agri Business program (AusABBA II)

The Australia Balochistan Agri Business program (AusABBA II) is financed by The Australian Government and implemented by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations in collaboration with the Government of Balochistan. The program covers 6 districts of South West Balochistan, near the Afghan/Iranian border, Chaghai, Kech, Kharan, Nushki, Panjgur and Washuk districts.
AusABBA is helping households engaged in agriculture in South Western Balochistan to adopt sustainable, profitable and diversified strategies in an enabling environment to increase their incomes, food security and nutritional status. AusABBA II trains male and female farmers and strengthens their supply chains and livelihoods and connects farmers with markets for Balochistan specific commodities such as onions, fruit trees, goat and sheep meat, seed, wool and dates.
AusABBA II targets (organized) male and female subsistence and commercial farmers and mothers and young children in the Districts, but also input suppliers, traders and middlemen.
Duration: 6 years (2017 – 2023)
Resource Partner(s): Australian Government (DFAT)
Budget: USD16.9 million
Implementing Partner(s): Government of Balochistan Livestock and Dairy Development Department, GoB Department of Agriculture and Cooperatives and GoB Planning and Development Department.
Beneficiaries (approximate number):
5,000 farmers and their households (total 6 Districts, 1st 3 years only)
Alignment to SDGs:



Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
SO 2 - Increase and improve provision of goods and services from Agriculture, forestry and fisheries in a sustainable manner
SO 4 - Enable inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems
The Alternative Livelihood Option Project explores potential alternative livelihoods options in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by engaging the communities to develop agricultural value chains by increasing capacities of value chain actors, service providers, and prom

The project identifies alternative high value crops which will contribute to increasing livelihood opportunities and economic growth for the Tribal and Torghar Districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
ALOP is introducing viable fruit, vegetable and flower production options, develop linkages to markets and promote value addition. The beneficiaries are selected based on baseline assessment/GIS mapping and in collaboration with the provincial secretariat and district administration. The key areas of influence will be diversification into high value crops, increased productivity, reduced post-harvest losses, value addition, improved marketing and diversification of markets, Farmer Marketing Collectives (FMCs) and Farm Business Schools (FBSs). Women Enterprise Groups (WEGs) will be organized to help build strong market linkages.
The project aims to contribute to improved and increased access to on-farm and off-farm livelihood opportunities, identify and introduce alternative high value crops in Bajaur, Khyber and Mohmand Districts and in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Tor Ghar District) in order to substitute poppy cultivation.
Duration: December 2018 - July 2020
Resource Partner(s): U.S. Bureau of International Narcotics and Law Enforcement Affairs (INL)
Budget: USD 793 000
Implementing Partner(s): FAO
Beneficiaries (approximate number):
1023 ( 900 producers, 53 market intermediaries, 20 women processors, 50 Government staff and facilitators)
Alignment to SDGs:



Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
- Make agriculture, forestry and fisheries more productive and sustainable
- Reduce rural poverty
- Enable inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems
The Horticultural Advancement Activity (THAzA)

THAzA increases access to on-farm and off-farm income opportunities, leading to sustainable economic growth. As an agribusiness investment venture it enhances competitiveness along stone and pome fruits, grapes, vegetable, and potato value chains, from production clear up to markets. It works along select Districts of the highlands of the Pakistan-Afghanistan border, and across a vast stretch of the Province of Balochistan.
THAzA addresses critical issues within these value chains such as high post-harvest losses, low profitability, low levels of value addition, and disregard of quality standards and thus inability to meet corporate buyers’ requirements. It also augments capacities of agriculture extension and business advisory services. THAzA particularly focuses on improving technical skills, advancing innovative technologies, and improving agricultural production practices through building skills of all value chain actors.
Duration: 5 years (July 20018 – June 2023)
Resource Partner(s): USAID
Budget: USD 16.2 million
Implementing Partner(s): Private sector, government agencies, academic community
Beneficiaries (approximate number): 22,126
Alignment to SDGs:



Alignment to FAO Strategic Objectives:
SO 4 - Enable more inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems
