The State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture presents the first global assessment of biodiversity for food and agriculture worldwide. Biodiversity for food and agriculture is the diversity of plants, animals and micro-organisms at genetic, species and ecosystem levels, present in and around crop, livestock, forest and aquatic production systems. It is essential to the structure, functions and processes of these systems, to livelihoods and food security, and to the supply of a wide range of ecosystem services. It has been managed or influenced by farmers, livestock keepers, forest dwellers, fish farmers and fisherfolk for hundreds of generations.
Prepared through a participatory, country-driven process, the report draws on information from 91 country reports to provide a description of the roles and importance of biodiversity for food and agriculture, the drivers of change affecting it and its current status and trends. It describes the state of efforts to promote the sustainable use and conservation of biodiversity for food and agriculture, including through the development of incentives to overcome adoption barriers within supporting policies, legal frameworks, institutions and capacities. It concludes with a discussion of needs and challenges in the future management of biodiversity for food and agriculture.
The report complements other global assessments prepared under the auspices of the Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, which have focused on the state of genetic resources within particular sectors of food and agriculture.
Presenting FAO's work to support countries and partners and contribute to mainstreaming biodiversity in agriculture, fisheries and forestry through projects and programmes across the globe. It also introduces the Biodiversity Mainstreaming Platform, led by FAO, in collaboration with the Convention for Biological Diversity (CBD), and other UN organizations and partners. The platform aims to turn rich and varied knowledge into actionable recommendations. It will facilitate the integration of actions for the conservation, sustainable use, management and restoration of biological diversity across agricultural sectors at national, regional and international levels. This includes the role of good governance, enabling frameworks, sound monitoring and incentives for ecosystem services.
Guidelines for decision-makers responsible for integrating the goals and targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development into national policies and programmes. Complementing FAO's Common Vision for Sustainable Food and Agriculture and its five principles, this publication presents 20 practical and interconnected actions with the aim of transforming food and agriculture and driving achievement across the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This includes the use of incentives for ecosystem services to support biodiversity conservation, resilient and sustainable consumption and production, and develop innovative livelihoods.
FAO is leading efforts to improve food security and nutrition through integrated approaches on the ground. These initiatives are based on the resilience and social equity of communities, and preserving the natural resource base upon which all food production depends. We know we can meet the challenge of ending hunger, and support sustainable livelihoods of people and communities who produce food. However, to be successful we must simultaneously address challenges that are both natural resource-based and socio-economic in nature, the origins of which may stem far from affected communities. This requires integrated investments at scale and across domains.
This publication presents FAO’s key initiatives in support of the landscape approach, and represents an important step in consolidating these knowledge resources in support of country commitments to the Sustainable Development Goals.
Sustainable agriculture for biodiversity: Biodiversity for sustainable agriculture
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in food security, nutrition, livelihoods and in the provision of ecosystem services. Agriculture is a major user of biodiversity but also has the potential to contribute to the protection of biodiversity. Today’s key challenge is how to increase production to meet the growing demand for food, feed and bioenergy while conserving biodiversity and reducing the pressure on natural resources and ecosystems. Good governance, enabling frameworks, and stewardship incentives are needed to facilitate mainstreaming of biodiversity
Incentives for Ecosystem Services (IES) is an example of FAO's work to support biodiversity conservation. The IES approach is noted as a key step in the future to integrate agriculture and the conservation of natural resources, and to support farmers in the transition to sustainable best practices. This includes: mapping of existing initiatives and mechanisms to mainstream biodiversity conservation across sectors; encouraging of responsible private sector investment to co-finance incentives to promote sustainable practices, and; supporting countries develop cross-sectoral 'packages of actions' that include improved and enforceable legal frameworks, and socio-economic incentives to reduce opportunity costs of biodiversity conservation for poor farmers, livestock keepers, fishers and forest managers.
Mainstreaming ecosystem services and biodiversity into agricultural production and management in the Pacific Islands
The role of Incentives for Ecosystem Services (IES) to support the management of and mainstreaming of biodiversity and ecosystem services into agriculture, at the national level, in the Pacific Islands are addressed in this technical guidance document. Specifically, the use of coordinated incentives through IES packages to support ecosystem services through sustainable production to assist countries in developing and implementing their National Biodiversity Strategy Action Plans (NBSAPs)
The ecosystem services series: The contributions of livestock species and breeds to ecosystem services
Livestock play a special role in the provision of ecosystem services and are an essential part of many agro-ecosystems. They do so by transforming feeds into nutritious foods and useful products for human consumption, direct interaction with ecosystems and mobility, enabling their response to resource availability and climate.
Incentives for Ecosystem Services (IES) are discussed as an approach to understand, value and provide incentives for farmers to sustainably manage their livestock to protect ecosystem services and biodiversity.
This document describes the opportunities, risks and motivation for the private sector to engage in landscape investment.
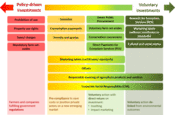
Incentives spectrum
The Incentives for Ecosystem Services (IES) spectrum describes the range of incentives, ranging from mandatory regulations based on the polluter-pays principle to voluntary investments in the environment based on the provider-gets principle. The spectrum illustrates the variety of incentives that can be used in the context of agriculture and environment sector to influence producer and consumer behaviour.