Fish loss in the artisanal fisheries subsector in Tumaco, Colombia
Food loss is defined as the reduction in the quantity or quality of food throughout a part of the food supply chain – from harvest to wholesale marketing. It is the result of decisions and actions from suppliers in the chain and is recognized as a distinct part of waste because the drivers that generate it and the solutions are different. A 2020 estimate for the Colombian Amazon revealed that roughly 33 percent of the output of the artisanal fishing value chain in Leticia was lost (14.8 percent while fishing; 18.2 percent during marketing).
In 2023, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the José Benito Vives de Andreís Institute for Marine and Coastal Research (INVEMAR) conducted a pilot study in Colombia to assess fish loss and identify multidimensional solutions. This led to the creation of the Interinstitutional Panel on Aquatic Food Losses and Waste (PIPDA) in October 2023, with national actors validating the information and providing both technical and financial inputs for the implementation of solutions to reduce these types of losses.
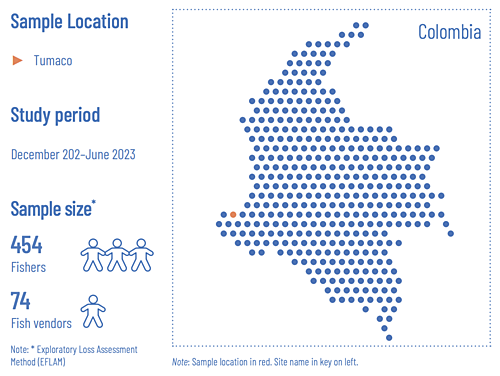
Tumaco was chosen as PIPDA’s pilot location in Colombia. Tumaco is located on the Pacific coast of Colombia in the department of Nariño. The rural area is territorially organized into Community Councils of Black Communities, which are located in river areas where the population has traditionally lived. Indigenous Peoples reside in reserves belonging to the Awá community.
Methodology
Qualitative evaluation (EFLAM): The fieldwork was carried out in 2023 from January 23 to January 27 by researchers from INVEMAR using the Exploratory Loss Assessment Method (EFLAM).
Evaluation with a gender perspective (GRFLAM): In meetings with 13 focus groups, detailed information was collected for gender analysis in the value chain using the Gender-Responsive Fish Loss Assessment Method (GRFLAM). Participants included 84 people (51 men and 33 women) linked to the value chain.
Quantitative analysis (QLAM): These methods included semi-structured interviews, application of pilot surveys, observation checklists and photographic records taken in the field and constructed under ArcGIS Survey® (Version 3.13.249), using the Questionnaire Loss Assessment Method (QLAM). In total, 422 interviews were
Results
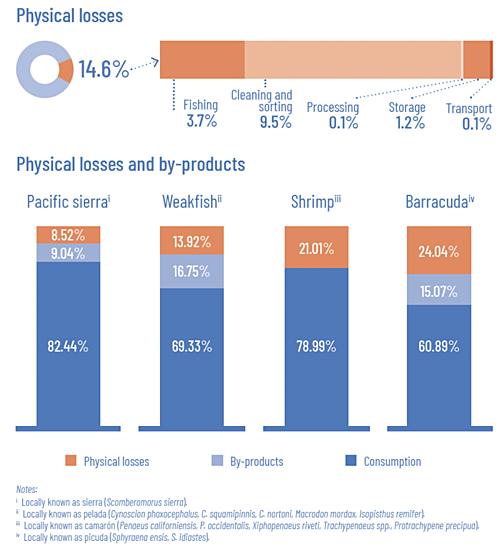
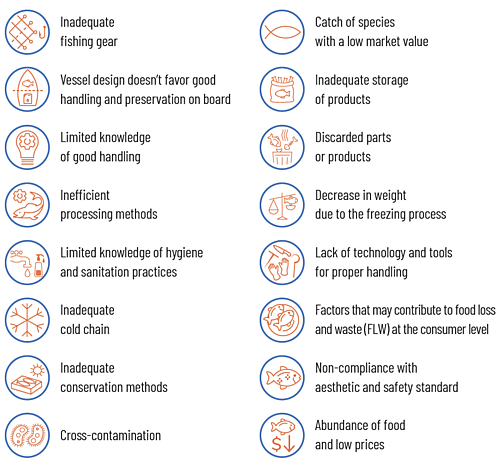
Major causes of loss
Additional related materials and articles
Multidimensional solutions to reduce losses and waste of fish in Colombia
Fish loss in the artisanal fisheries subsector in Tumaco, Colombia



