Latest stories

Salty soil adventures - A collection of ten children’s stories from around the world
13/07/2022
In the framework of World Soil Day (WSD) 2021, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS) and the Global Soil Partnership (GSP) launched a scientific children's booklet contest on salt-affected soils with the motto "Halt soil salinization, boost soil productivity".

Moving forward for a sustainable management of salt-affected soils
09/05/2022
The Global Symposium on Salt-Affected Soils (GSAS21) – “Halt soil salinization, boost soil productivity” addressed one of the most acute soil threats worldwide, soil salinization and sodification, which challenges the sustainable development of countries with arid and semiarid climates and extensive coastal areas.

World map of salt-affected soils launched at virtual conference
20/10/2021
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) today launched the Global Map of Salt-Affected Soils, a key tool for halting salinization and boosting productivity. The map estimates that there are more than 833 million hectares of salt-affected soils around the globe (8.7% of the planet).

2nd Meeting of the International Network on Salt-affected Soils INSAS | Uzbekistan, May 2023
20/10/2021
The salinization and sodification of agricultural land is increasing due to climate change, water shortages, and unsustainable farming practices. Forecasts indicate a 23 percent increase in global drylands by the end of the 21st century..

Vote for your favourite GSAS21 scientific poster!
22/10/2021
With nearly 70 000 votes in less than 48 hours the scientific poster contest was a great success! Poster number 49: ‘Sustainable rehabilitation, bridging yield gaps and increasing farmers’ income in salt affected rice–wheat agroecosystems: a farmers’ participatory assessment’ by Parvender Sheoran won the 1st prize with 4 546 votes.

Novel initiative to map salt-affected soils globally
06/04/2020
Salt-affected soils (SAS) are a group of soils with high content of neutral salt and/or sodium ions. The salts hold water and nutrient in soil at high tension, which make these vital components practically unavailable for plants at the rootzone.

Launch of the international network of salt-affected soils
21/11/2019
On the occasion of the ICBA 20th anniversary celebrations, the Global Forum on Innovations for Marginal Environments was organized in view of the major impact of soil and water salinization and climate change on ecosystems, agricultural productivity, livelihoods and food security worldwide.
Soil salinity mapping and trainings
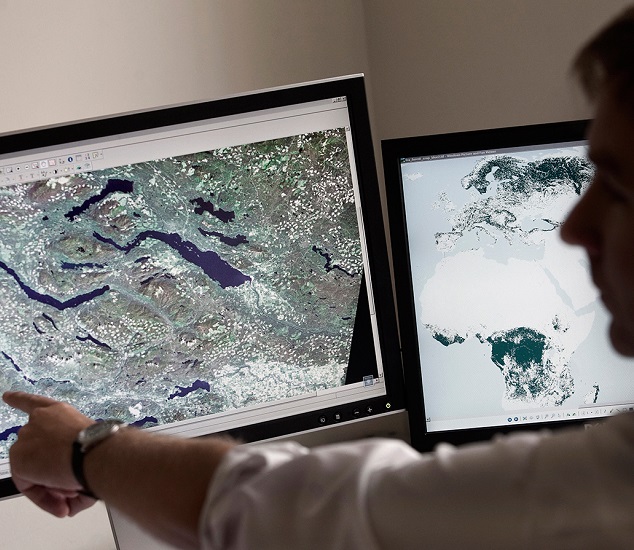

Global Soil Salinity map released
Launched on 20 October 2021
FAO-GSP launched the Global Soil Salinity map (GSASmap) to update the global and country-level information on salt-affected soils and lay ground for future periodic monitoring.
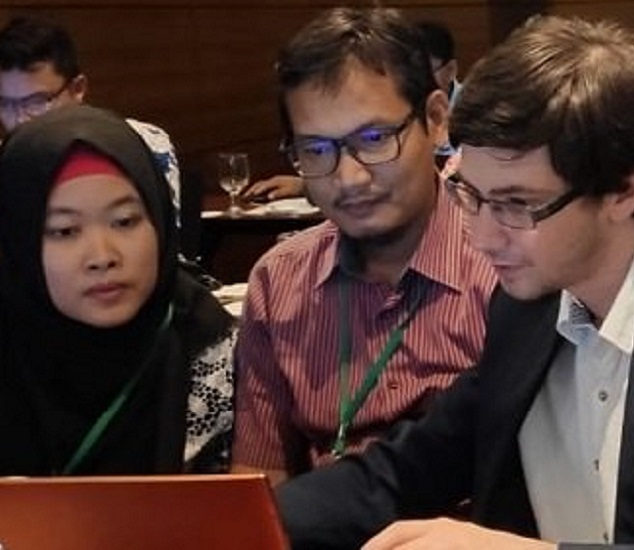

Global Soil Salinity Trainings
Capacity development at global scale
Through eight regional trainings, the capacity development programme organized by FAO-GSP, reached 70 countries and 400 experts with the objective to produce a global salinity map.
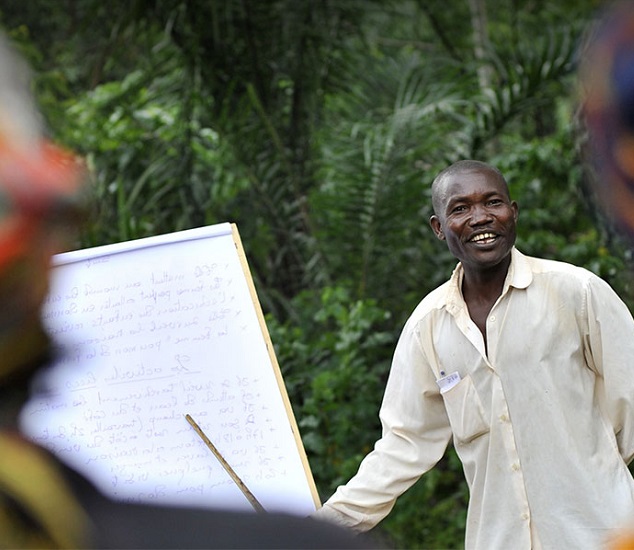

Soil Doctors and Salinity
Salinity in farmer-to-farmer trainings
The programme provides soil doctors with training, educational material and soil testing kits to build capacity on the principle of soil science and promote sustainable soil management.
Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils
FAO publication on the global status of salt-affected soils
The report on the Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils is focused on the salt-affected soils extent and intensity of salt levels in the soil at the national, regional and global scales.
In action

Global Symposium on Salt-affected Soils
20-22 October 2021, Virtual format
The Symposium was a science-policy meeting, organized by FAO-GSP, ITPS, SPI-UNCCD, the Government of the Republic of Uzbekistan, the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS), the International Center on Biosaline Agriculture (ICBA), the International Network of Salt-Affected Soils (INSAS), and the Global Framework on Water Scarcity in Agriculture (WASAG).

International Network on Salt-affected Soils
Launched at the Center on Biosaline Agriculture
The International Network of Salt-Affected Soils (INSAS), launched during ICBA's first Global Forum on Innovations for Marginal Environments, aims to facilitate the sustainable and productive use of salt-affected soils for the current and future generations.

Capacity development saline soil management
Handbook and training on salinity in Eurasia
The capacity development training organized by FAO-GSP, Eurasian Center for Food Security, NSC ISSAR was held on 26-29 September 2017 in Kharkiv, Ukraine for Eurasia with the objective to train on efforts and technologies to sustainably manage saline soils.

Call for projects for Eurasian countries
FAO-GSP and Eurasian Center for Food Security
Eurasia characterizes for salt-affected soils that put at risk food security and the achievement of the SDGs. Two calls for projects on soil research and on soil salinity mitigation and adaptation are launched annually to facilitate targeted research and partnerships.
Multimedia
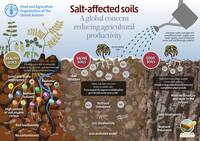
Salt-affected Soils: A global concern reducing agricultural productivity
Soils affected by salinity and sodicity undergo a rapid decline of health, losing their capacity for biomass production, natural filtration, carbon sequestration and other necessary ecosystem functions.

Global Symposium on Salt-affected Soils
This high-level science-policy meeting #GSAS21 “Halt soil salinization, boost soil productivity” will be held in a virtual format from 20 to 22 October 2021.
Are all salt-affected soils a threat?
The differences between naturally saline and sodic soils and human-induced salinization and sodification.
Economical losses due to soil salinization
The global annual cost of salt-induced land degradation in irrigated areas is estimated to be USD 27.3 billion related to lost crop production.
Migration due to soil salinization
As climate change and water scarcity increase, more soils become salt-affected...forcing people to leave their once productive land and migrate.
What can you do? Halt soil salinization, Boost soil productivity
Raise awareness, promote the use of sustainable farming systems, invest in gathering better knowledge...
Farmers in action
Eight good practices to halt soil salinization and boost soil productivity: Practice halophytic agriculture, irrigate with good quality water...
Related publications
Status of the World's Soil Resources. Main report and Technical summary (EN | ES | FR)