Healthy marine ecosystems are vital to the planet’s well-being and realization of sustainable blue economies. Marine ecosystems help maintain livelihoods, bolster food security, mitigate climate change, strengthen resilience, and conserve globally significant biodiversity. Coastal marine hypoxia, oxygen depletion leading to "dead zones", is a serious and rapidly expanding environmental threat to these shared global values. Today, hundreds of hypoxia zones suffocate marine life across millions of square kilometers with extreme benthic mortality and catastrophic fish die-offs. With the threat of coastal marine hypoxia growing quickly and quietly, there is an urgent need to accelerate targeted knowledge, policy, financing, and best management practices to avoid continued depletion of marine biodiversity across our shared oceans.
The objective of the Clean and Healthy Ocean Integrated Program (CHOIP), led by FAO in partnership with ADB, EBRD, CAF, UNESCO/IOC and GWP, is to address marine hypoxic zones by curbing coastal pollution from agriculture, industrial and municipal sources through policy and regulatory measures and infrastructure investments combined with nature-based solutions. In doing so, the program will foster the enabling environment to advance countries’ efforts toward sustainable blue economy goals. The CHOIP will catalyse a transformative change by expanding upon the current baseline and promoting existing national and large marine ecosystems (LME) capacities, capture emerging innovative funding opportunities and scale up effective programming supported by GEF and others.
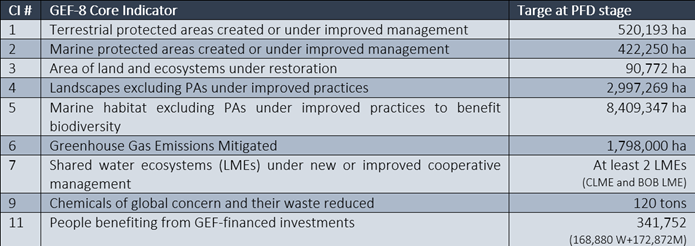
CHOIP Core Indicators