1. What are Farmers’ Rights under the International Treaty?
1. What are Farmers’ Rights under the International Treaty?
The Preamble of the International Treaty states that “the past, present and future contributions of farmers in all regions of the world, particularly those in centres of origin and diversity, in conserving, improving and making available these resources, is the basis of Farmers’ Rights.”
The Preamble further states that “the rights that are recognized in this Treaty to save, use, exchange and sell farm-saved seed and other propagating material, and to participate in decision-making regarding, and in the fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising from, the use of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture, are fundamental to the realization of Farmers’ Rights, as well as the promotion of Farmers’ Rights at national and international levels.”
These elements form the basis of the measures contained in Article 9 of the International Treaty, along with the protection of traditional knowledge relevant to plant genetic resources for food and agriculture (PGRFA). Farmers’ Rights, as contained in Article 9 of the International Treaty, can be illustrated as follows:
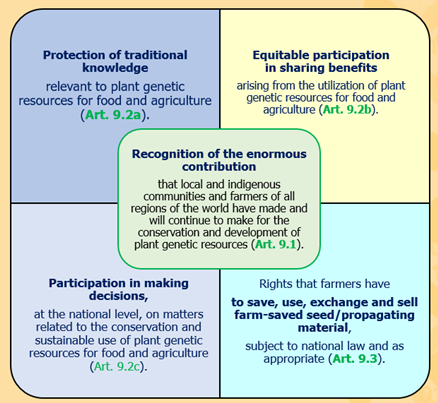
2. How does the International Treaty support Farmers’ Rights?
2. How does the International Treaty support Farmers’ Rights?
The International Treaty is one of the first legally-binding international instruments that explicitly acknowledges the enormous contribution of farmers and indigenous communities to developing and managing the world’s crops and other PGRFA, which constitute the basis of our food supply. They have taken care of the world’s PGRFA for millennia. And they will continue to contribute to the conservation and sustainable use of these resources in the future. In recognition of this contribution, Article 9 of the International Treaty is devoted to Farmers’ Rights.
The International Treaty acknowledges Farmers’ Rights and calls for (i) the traditional knowledge of these farmers to be protected; (ii) their increased participation in national decision-making processes; and (ii) assurances that they will share in the benefits from the use of these resources.
The International Treaty calls on its Contracting Parties and all nations to protect and promote the rights of smallholder farmers, particularly in terms of protecting their rights to their seeds, and their involvement in relevant national decision-making.
In accordance with Article 9 of the International Treaty, the responsibility to protect, promote and realize these Farmers’ Rights rests with national governments through a number of suggested measures, and by providing farmers with a basis from which to advocate for their rights.
3. Who can promote the implementation and realization of Farmers’ Rights?
3. Who can promote the implementation and realization of Farmers’ Rights?
Everyone can promote the implementation and realization of Farmers’ Rights in their professional and institutional capacity, including Contracting Parties of the International Treaty, local and indigenous communities and farmers, research and academic institutions, civil society organizations, the public and private sector, funding institutions, and interested stakeholders.
Examples and options to promote, encourage and guide the implementation of Farmers’ Rights, as set out in Article 9 of the International Treaty, see link in Question 4.
4. Are there existing examples of practices, measures and experiences leading to the realization of Farmers’ Rights?
4. Are there existing examples of practices, measures and experiences leading to the realization of Farmers’ Rights?
Yes. The Inventory of national measures, best practices, and lessons learned from the realization of Farmers’ Rights, as set out in Article 9 of the International Treaty, presents a catalogue of measures and practices. It was developed by the Ad Hoc Technical Expert Group on Farmers’ Rights,[1] based on its mandate from the Governing Body at its Seventh Session. The examples are organized into 11 categories:
- Recognition of local and indigenous communities’, farmers’ contributions to conservation and sustainable use of PGRFA, such as awards and recognition of custodian/guardian farmers.
- Financial contributions to support farmers’ conservation and sustainable use of PGRFA, such as contributions to benefit-sharing funds.
- Approaches to encourage income-generating activities to support farmers’ conservation and sustainable use of PGRFA.
- Catalogues, registries and other forms of documentation of PGRFA and protection of traditional knowledge.
- In situ/on-farm conservation and management of PGRFA, such as social and cultural measures, community biodiversity management and conservation sites.
- Facilitation of farmers’ access to a diversity of PGRFA and protection of traditional knowledge.
- Participatory approaches to research on PGRFA, including characterization and evaluation, participatory plant breeding and variety selection.
- Farmers’ participation in decision-making at local, national, subregional, regional and international levels.
- Training, capacity development and public awareness creation.
- Legal measures for the implementation of Farmers’ Rights, such as legislative measures related to PGRFA.
- Other measures/practices.
For an updated list of measures and practices related to implementing Farmers’ Rights, and to learn more about this, visit our dedicated page: www.fao.org/plant-treaty/areas-of-work/farmers-rights/overview-inventory/en/
[1] www.fao.org/plant-treaty/areas-of-work/farmers-rights/expert-group/en/
5. Are there options to encourage, guide and promote the realization of Farmers’ Rights?
5. Are there options to encourage, guide and promote the realization of Farmers’ Rights?
Yes. There are many options.
The International Treaty document: Options for encouraging, guiding, and promoting the realization of Farmers' Rights as set out in Article 9 of the International Treaty provides numerous options based on actual measures, best practices and experiences of the Contracting Parties and stakeholders from across the globe.
The Ad hoc Technical Expert Group on Farmers’ Rights[1] developed the Options, drawing on the experiences of Contracting Parties and stakeholders, as shared in the Inventory.
[1]A group of experts established by the Governing Body in 2017. Detailed information about it can be found here: www.fao.org/plant-treaty/overview/governing-body/committees/ahteg/en/
6. How can I submit measures, experiences, practices and lessons learned on implementing Farmers’ Rights?
6. How can I submit measures, experiences, practices and lessons learned on implementing Farmers’ Rights?
Contracting Parties, farmers' organizations, stakeholders and relevant organizations may submit their practices and experiences on implementing Article 9 of the International Treaty by using the template for submission. The template is available in four languages: English, French, Spanish, and Arabic.
7. I want to know more about Farmers’ Rights and their current development.
7. I want to know more about Farmers’ Rights and their current development.
Recent developments on the implementation of Farmers’ Rights are available on the International Treaty page: www.fao.org/plant-treaty/areas-of-work/farmers-rights/en/
A series of educational modules including a Module on Farmers´ Rights is available on the International Treaty website. An interactive course on Farmers’ Rights is also available at the InforMEA Portal, where learners can obtain a certificate once they have passed the test!
To submit measures and practices, or for any queries, please contact the Secretariat by email: [email protected].

